| In vivo: |
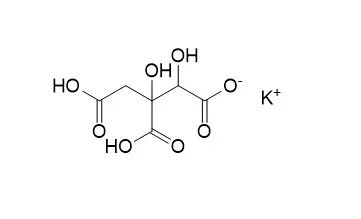
| Toxicol Mech Methods . 2010 Nov;20(9):515-525 | | Safety assessment of a calcium-potassium salt of (-)-hydroxycitric acid[Pubmed: 20946014] | | The safety of Garcinia cambogiaextract, its active ingredient (-)-hydroxycitric acid (HCA), and the marketed weight management formula, Super CitriMax(®) (HCA-SX), is supported by numerous in vitro and animal experimental studies as well as several clinical studies. HCA-SX has been shown to reduce appetite, inhibit fat synthesis, and decrease body weight. A series of toxicological tests including acute, short-term, and sub-chronic studies as well as teratogenicity/reproduction and genotoxicity studies were performed on HCA-SX. In the acute oral toxicity study, administration of a single dose of 5,000 mg/kg of HCA-SX did not reveal any significant changes for all examined tissues. Following the high dose safety testing, there were no remarkable changes or differences observed in any of the experimental conditions monitored. There were no macroscopic abnormalities for any examined tissues at scheduled necropsies. On the basis of these findings, the consumption of HCA-SX at dose level of up to 4667 mg/day is considered safe. | | J Med . 2004;35(1-6):33-48. | | An overview of the safety and efficacy of a novel, natural(-)-hydroxycitric acid extract (HCA-SX) for weight management[Pubmed: 18084863] | | Garcinia cambogia-derived (-)-hydroxycitric acid (HCA) is a safe, natural supplement for weight management. HCA is a competitive inhibitor of ATP citrate lyase, a key enzyme which facilitates the synthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol and triglycerides. Previous studies in our laboratories have demonstrated the superior bioavailability of a novel calcium-potassium salt of HCA derived from Garcinia cambogia (HCA-SX, Super CitriMax). Greater bioavailability of HCA-SX was observed when taken on an empty stomach. HCA-SX was also shown to exhibit concentration-dependent release of serotonin in isolated rat brain cortex, which may explain its appetite suppressive action. Acute oral, acute dermal, primary dermal irritation, primary eye irritation and 90-day chronic toxicity studies, as well as Ames bacterial reverse mutation and mouse lymphoma tests, were assessed to determine the safety of HCA-SX. In the 90-day toxicity study, dose- and time-dependent effects of HCA-SX were assessed on body weight, selected organ weights, hepatic and testicular lipid peroxidation and DNA fragmentation, hematology and clinical chemistry, and histopathology in male and female Sprague-Dawley rats. No remarkable toxicity results were detected, demonstrating the safety of HCA-SX. Furthermore, clinical studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of HCA-SX over a period of eight weeks were conducted in 60 human volunteers. Subjects were given a 2,000 kcal diet/day, participated in a 30 min walking exercise program 5 days/week and given an oral dose of placebo or 4666.7 mg HCA-SX (providing 2,800 mg HCA) in three equally divided doses 30-60 min before meals, Body weight, BMI, lipid profiles, serum leptin, serotonin and excretion of urinary fat metabolites were determined at 0, 4 and 8 weeks of treatment. At the end of 8 weeks, body weight and BMI decreased by 5.4% and 5.2%, respectively. Food intake, total cholesterol, LDL, triglycerides and serum leptin levels were significantly reduced, while HDL and serotonin levels, and excretion of urinary fat metabolites (a biomarker of fat oxidation) significantly increased. No significant adverse effects were reported. These results demonstrate the safety, bioavailability and efficacy of HCA-SX in weight management. | | Toxicol Mech Methods . 2008;18(5):443-451 | | Safety of a Novel Calcium/Potassium Saltof (-)-Hydroxycitric Acid (HCA-SX): II.Developmental Toxicity Study in Rats[Pubmed: 20020869] | | ABSTRACT (-)-Hydroxycitric acid (HCA), active constituent (10%-30%) of the dried fruit rind of Garcinia cambogia, is commonly used as a dietary supplement for weight management. The objective of the present study was to evaluate the teratogenic potential of a novel calcium/potassium salt of HCA (HCA-SX) in Sprague-Dawley rats. Due to its potential to affect fat synthesis and reduce food intake, processes that are often crucial in normal fetal development, this teratology study was undertaken as part of a multigeneration reproductive investigation. The animals in this study were selected randomly after weaning from each F(2b) litter of the F(1) generation from the two-generation reproductive toxicity study. To start the teratology study, Sprague-Dawley rat pups ( approximately 30/sex/group) from the F(2b) generation were allowed to grow up to 10 to 12 weeks of age before mating. The rats in the treatment group were exposed directly to HCA-SX through feed, while prior to their weaning, they had indirect exposure to the test material during lactation. The dietary exposure levels were the same as those employed for the two-generation reproductive toxicity study, viz. 1000, 3000, or 10,000 ppm. Following mating at maturity, the pregnant rats were observed daily for clinical signs of adverse effects, and body weight and feed consumption were recorded. On day 20 of gestation, animals were subjected to a necropsy and cesarean section to examine the uterus, ovaries, and fetuses for assessment of different parameters of pregnancy and embryo-fetal defects. Despite a slight (13%) lowering of maternal body weight gain during gestation period in the group receiving 10,000 ppm HCA-SX, no evidence of maternal toxicity, adverse effects on the parameters evaluated for the gravid uteri, external abnormalities in the fetuses, soft tissue abnormalities in the fetuses, or skeletal abnormalities in the fetuses were noted. Based on the results of this developmental toxicity study, conducted in continuation of a two-generation reproductive toxicity study, HCA-SX was not found to be teratogenic in the Sprague-Dawley rat at the dietary exposure levels of 1000, 3000, and 10,000 ppm, equivalent to the dose levels of 103, 352, or 1240 mg/kg/day, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)