| In vitro: |
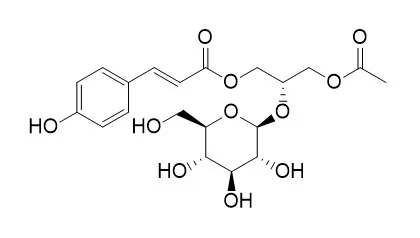
| Applied Biological Chemistry volume 60, pages527–533 (2017) | | Phenylpropanoids from Lilium Asiatic hybrid flowers and their anti-inflammatory activities[Reference: WebLink] | | Three phenylpropanoids were isolated from the flowers of Lilium Asiatic hybrids through repeated silica gel or octadecyl silica gel column chromatographies. The chemical structures were determined to be 1-O-trans-caffeoyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (1), regaloside A (2), and Regaloside B (3), based on spectroscopic data gathered from nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, electron ionization mass spectrometry (EI/MS), polarimetry, and infrared spectroscopy (IR) experiments. Compounds 1 and 2 showed significant DPPH radical scavenging activity of 60.1 and 58.0% at 160 ppm, respectively, compared with the 62.0% activity of the positive control, α-tocopherol. At a concentration of 50 μg/mL, compounds 1–3 inhibited the expression of iNOS to 4.1 ± 0.01, 70.3 ± 4.07, and 26.2 ± 0.63, respectively, and decreasing COX-2 expression to 67.8 ± 4.86, 131.6 ± 8.19, and 98.9 ± 4.99. Also, at the same concentration, compounds 1–3 decreased the ratio of p-p65/p-65 to 43.8 ± 1.67, 40.7 ± 1.30, and 43.2 ± 1.60, respectively, and the expression of VCAM-1 to 42.1 ± 2.31, 48.6 ± 2.65, and 33.8 ± 1.74, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)