| In vitro: |
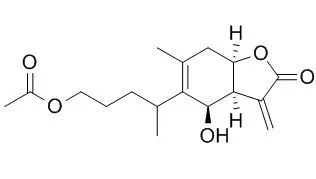
| Acta Phytophylacica Sinica, 2008 , 35 (6) :551-6. | | Separation and analysis of 1-O-acetylbritannilactone from Inula japonica and determination of antifungal activity[Reference: WebLink] | In order to clarify the main antifungal compound of Inula japonica,the chloroform extraction of crude extract from I.japonica flowers was separated and compound 1-O-Acetyl britannilactone (ABL) was obtained.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The content of the compound ABL in flowers crude extract was tested with high performance liquid chromatography.The inhibitory effects of compound ABL against Sphaerotheca fuliginea,Pseudoperonospora cubensis,Botrytis cinerea,Alternaria solani and Phytophthora infestans were tested.The chemical structure of ABL reference substance was elucidated by using ultraviolet spectrometry(UV),infrared spectroscopy(IR),nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR).The purity of ABL reference substance was 99.5%,which satisfies the need of reference substances of traditional Chinese medicines.A method of high performance liquid chromatography was used for the determination of the content of ABL in crude extract from I.japonica flowers(it's 2.45%),then the content of ABL in I.japonica was calculated(it's about 0.25%).
CONCLUSIONS:
Inhibitory activities of compound ABL against the five phytopathogenic fungi were different,which against the cystospore germination of P.infestans was significant,the inhibition rate was 100% at the concentration 0.1 mg/mL. | | Chinese Journal of Cell Biology, 2007 , 29 (2) :267-71. | | 1-o-acetylbritannilactone Inhibits Inflammatory Response by Suppressing NF-κB Activation[Reference: WebLink] | Immunocytochemistry and Western blot analysis were adopted to measure the nuclear translo-cation of NF-κB p65 and the expression of IκB-α, cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) was performed to detect DNA-binding activity of NF-κB in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMC) pre-treated with ABL. Western blot and immunocytochemistry analysis showed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment resulted in increasing nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65, and declining levels of IκB-α in VSMC. However, 1-O-Acetyl britannilactone (ABL) pretreatment inhibited the nuclear translocation of p65 and degradation of IκB-α in-duced by LPS, and the inhibitory effect of ABL was concentration-dependent. LPS increased the binding of nuclear extracts from VSMC induced by LPS to double strands oligonucleotide probe containing NF-κB binding site using EMSA. The shift bands were abolished when a 100-fold excess of unlabeled NF-κB oligonucleotide probe was included. Pretreatment with ABL significantly reduced the nuclear level of NF-κB and declined the binding activity of nuclear extracts with DNA probe induced by LPS. Furthermore, ABL consequentially inhibited the expression of NF-κB-dependent COX-2 gene induced by LPS.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that ABL may be one anti-inflammatory drug which inhibits the expression of COX-2 gene by blocking NF-κB activation and thus suppresses the inflammatory response to LPS in VSMC. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)