| In vitro: |
| Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2013, 44(18): 2502-7. | | Anti-complementary anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum and their action targets.[Reference: WebLink] | To study the anti-complementary anthraquinones from Polygonum cuspidatum and their action targets.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
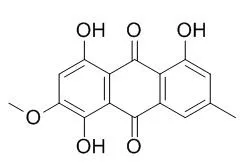
The anti-complementary activity-directed isolation was carried out with the hemolysis test as guide. All isolates were evaluated for their in vitro anti-complementary activities. The action targets of the main bioactive constituents were also examined using complement-depleted sera. Ten anthraquinones and three other compounds were isolated from the EtOAc fraction of P.cuspidatum extract, including physcion(1), chrysophanol(2), questin(3), emodin-8-O-β-D-glucoside(4), emodin(5), rhein(6),fallacinol(7), citreorosein(8), Xanthorin(9), isorhodoptilometrin(10), 2, 5-dimethyl-7-hydroxychromone(11), 7-hydroxy-4-methoxy-5-methylcoumarin(12), and 5, 7-dihydroxy-1-isobenzofuranone(13). Compounds 9 and 10 were isolated from the the plants of Polygonaceae for the first time, and compound 9 was the alizarin-type anthraquinone first obtained from P. cuspidatum. Compounds3—9 showed the anti-complementary activity in different degrees, and compound 7 exhibited the most significant activity against the classical and alternative pathway [CH50=(6 ± 2) μg/mL, AP50=(50 ± 5) μg/mL]. The study on the preliminary mechanism revealed that compound 4 interacted with C1q, C2, and C9 in complement activation cascade, while compound 7 acted on C1q, C2, C4, and C9.
CONCLUSIONS:
The anthraquinones are main anti-complementary constituents in P. cuspidatum; and fallacinol(7) is a potential complement inhibitor with strong activity and definite targets, which should be further studied in future. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)