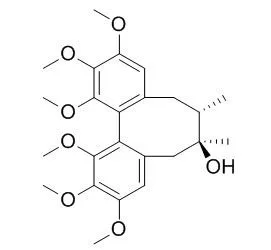
| Description: |
Schisandrol A may be a new promising treatment for neurotoxicity, erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease.It can inhibit the activities of Pgp,Beta Amyloid,CYP3A4,cGMP,and NOS, the IC(50) value of CYP3A4 is 32.02 microM.
|
| Targets: |
ERK | JNK | P450 (e.g. CYP17) | p38MAPK | Caspase |
| In vitro: |
| Zhong Yao Cai. 2010 Mar;33(3):397-401. | | Protective and therapeutic effects of schisandrol A on Abeta damaged PC12 cells.[Pubmed: 20681306] | To observe the protective and therapeutic effect of Schisandrol A on the Abeta damaged PC12 cells. PC12 cells were damaged by Abeta in vitro.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Morphological changes were observed and the number of cells with neurite was analyzed by phase contrast microscope. The cell viability of PC12 cells was determined by the MTT method. Many dispirited cells with atrophied or fragmented neurites in the Abeta damaged PC12 cells were observed under the microscope. More vital cells with longer neurites were observed in the Schisandrol A treated PC12 cells and the number of cells with neurite increased. The difference of cell viability between the two groups was statistical significant.
CONCLUSIONS:
Schisandrol A can antagonize the neurotoxicity of Abeta and has protective and therapeutic efficacy on Abeta damaged PC12 cells. | | Breast Cancer . 2018 Mar;25 | | Schisandrin A reverses doxorubicin-resistant human breast cancer cell line by the inhibition of P65 and Stat3 phosphorylation[Pubmed: 29181822] | | Background: Multidrug resistance (MDR) in breast cancer therapy occurs frequently. Thus, anti-MDR agents from natural products or synthetic compounds were tested extensively. We have also explored the reverse effect and mechanism of Schisandrin A (Sch A), a natural product, on MCF-7 breast cancer doxorubicin (DOX)-resistant subline MCF-7/DOX.
Methods: MTT assay was performed to measure the viability of MCF-7 cells to assess the reverse effect of Sch A. Western blot analysis was used to study the protein levels. Laser scanning confocal microscopy was performed to detect the intercellular DOX and Rhodamine 123 accumulation. The qRT-PCR was used to analysis the target gene expression. Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to test the transcriptional activity of P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
Results: Sch A, at the concentration of 20 μM, showed selective reverse effect (better than the positive control, verapamil at 5 μM) on MCF-7/DOX cell line but not on BEL-7402/DOX, Hep G2/DOX, and K-562/DOX cells. In addition, Sch A enhanced DOX-induced cleavage of Caspase-9 and PARP levels by increasing intracellular DOX accumulation and inhibiting P-gp function. Furthermore, Sch A selectively suppressed P-gp at gene and protein levels in MCF-7/DOX cells which express high level of MDR1 but not MRP1, MRP3, or BCRP. Besides, Sch A showed inhibitory effect on P-gp transcriptional activity. Sch A significantly reduced p-IκB-α (Ser32) and p-Stat3 (Tyr705) levels which mediate P-gp expression. In addition, Stat3 knockdown enhanced the reverse effect of siP65. The combined effect of siStat3 and siP65 was better than Sch A single treatment in MCF-7/DOX cells.
Conclusion: Sch A specifically reverses P-gp-mediated DOX resistance in MCF-7/DOX cells by blocking P-gp, NF-κB, and Stat3 signaling. Inhibition of P65 and Stat3 shows potent anti-MDR effect on MCF-7/DOX cells.
Keywords: Doxorubicin; Multidrug resistance; NF-κB; Schisandrin A; Stat3. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2016 Mar 31;62(3):115-9. | | Cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation induced by Schisandrol A via the NO-cGMP signaling pathway.[Pubmed: 27064883] | To evaluate the effect of Schisandrol A on rabbit corpus cavernosum smooth muscle and elucidate the potential mechanism. Penises were obtained from healthy male New Zealand White rabbits (2.5-3.0 kg).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The pre-contracted penis with phenylephrine (Phe, 10 μM) was treated with accumulative concentrations of Schisandrol A (10-7, 10-6, 10-5 and 10-4 M). The change in intracavernosum pressure (ICP) and tension was recorded, cyclic nucleotides in the cavernosum tissue were measured by radioimmunoassay, mRNA level and expression of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and neuronal NOS (nNOS) were measured by real time PCR and western blot respectively.
The corpus cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation induced by Schisandrol A was in a dose-dependent manner. Pre-treatment with NOS inhibitor (Nω nitro-L-arginine-methyl ester, L-NAME) or guanylyl cyclase inhibitor (1H-(1,2,4)oxadiazolo(4,3-a)quinoxalin-1-one, ODQ) significantly diminished the relaxation. The cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) level was significantly increased in the cavernosum tissue. Real time PCR and western blot showed the mRNA level and expression of eNOS and nNOS was also upregulated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Schisandrol A relaxes the cavernosum smooth muscle by activating NO-cGMP signaling pathway. It may be a new promising treatment for erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular disease. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)