| In vitro: |
| Phytomedicine. 2009 Dec;16(12):1144-50. | | Vasodilatory actions of xanthones isolated from a Tibetan herb, Halenia elliptica.[Pubmed: 19403292 ] | In this study, six major xanthones, isolated and identified from Halenia elliptica were investigated for their vasodilatory actions in isolated rat coronary artery.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
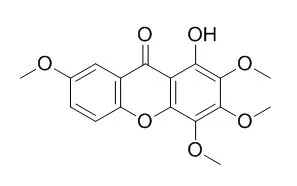
The xanthones, including 1-hydroxy-2,3,5-trimethoxy-xanthone (HM-1), 1-hydroxy-2,3,4,7-tetramethoxy-xanthone (HM-2), 1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxy-xanthone (HM-3), 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxy-xanthone (HM-4), 1,5-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-xanthone (HM-5) and 1,7-dihydroxy-2,3-dimethoxy-xanthone (HM-7) caused vasodilation in the coronary artery pre-contracted with 1 microM 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), with EC(50) values ranging from 1.4+/-0.1 microM (HM-1) to 6.6+/-1.4 microM (HM-2). The EC(50) values of the other xanthones were between those of HM-1 and HM-2. Removal of endothelium of the coronary artery led to decreases in the vasorelaxant effects of HM-1, HM-7 but not HM-2, HM-3, HM-4 and HM-5.
CONCLUSIONS:
Our results showed that xanthones isolated from Halenia elliptica are vasoactive substances which exhibit either endothelium-dependent or endothelium-independent mechanisms in rat coronary artery. The potency and mechanism(s) of the vasorelaxant effects of these xanthones may be relevant to the structure-activity differences in the level and the position of the substituent groups with the primary xanthone structure. | | Arch Pharm Res. 2008 Jul;31(7):850-5. | | Inhibitors of bone resorption from Halenia corniculata.[Pubmed: 18704326 ] | Eleven xanthones (1-11), three flavonoids (12-14) and three secoiridoids (15-17) were isolated from the aerial parts of Halenia corniculata.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among those compounds, 1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyxanthone (1), 1-Hydroxy-2,3,4,7-tetramethoxyxanthone (2), 1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5,7-pentamethoxyxanthone (3), 1-hydroxy-2,3,5-trimethoxyxanthone (4), 1,8-dihydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyxanthone (7), and luteolin (12), at the concentration of 1 microg/mL, effectively inhibited the osteoclast differentiation in a co-culture system with mouse osteoblastic calvarial cells and bone marrow cells. Notably, compounds 1, 3, and 4 exhibited, in a dose-dependent manner, significant inhibition of osteoclast differentiation even at a low concentration (0.01 microg/mL). All the inhibitory compounds, except for compound 7, significantly reduced the pit formation on the dentine slice compared with the control group. For the survival of the mature osteoclasts, compounds 1-4 and 12 (1 microg/mL), significantly decreased the survival number through induction of cell apoptosis, and compound 4 exhibited a significant inhibitory effect on osteoclast survival even at the low concentration of 0.1 microg/mL. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)