| Animal Research: |
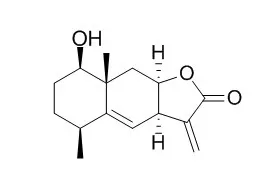
| Pharm Biol. 2015 May 28:1-7. | | 1β-Hydroxyalantolactone, a sesquiterpene lactone from Inula japonica, attenuates atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions induced by 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene in the mouse.[Pubmed: 26017682] | 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone (IJ-5) is a sesquiterpene lactone compound isolated from Inula japonica Thunb (Asteraceae). Sesquiterpene lactones have been shown to modulate many processes that influence inflammatory reactions. The present study examines the protective effect of 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone on atopic dermatitis (AD) in a mouse model induced by 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone was administrated intraperitoneally at 10 mg/kg 1 h before each DNCB challenge. RESULTS: 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone treatment attenuated DNCB-induced dermatitis severity and right ear swelling. The serum levels of IgE, IL-4, and IL-6 in 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone-treated mice were reduced by 54.7, 56.5, and 53.0%, respectively, while the mRNA levels of TNFα, IL-1, IL-4, and IL-6 in back skin lesions of 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone-treated mice were reduced by 47.7, 61.5, 57.5, and 58.5%, respectively, compared with untreated controls. Histopathological examination showed that 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone treatment decreased DNCB-induced hypertrophy, hyperkeratosis, and infiltration of inflammatory cells in both ear and back skins. Moreover, 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone suppressed the expression of TNFα, IL-1, and IL-6 with IC50 values of 6.58, 9.48, and 7.01 μM, respectively, and inhibited the activation of NF-κB pathway in TNFα-stimulated HaCat cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
The present study demonstrates the protective effects of 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone against AD-like skin inflammation and highlights 1beta-Hydroxyalantolactone as a potential therapeutic agent for AD. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)