| Structure Identification: |
| Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 May 15;56(21):5844-5848. | | Bioinspired Asymmetric Synthesis of Hispidanin A.[Pubmed: 28332749 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
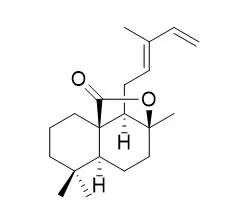
The first enantiospecific synthesis of hispidanin A (4), a dimeric diterpenoid from the rhizomes of Isodon hispida, was achieved with a longest linear sequence of 12 steps in 6.5 % overall yield. A key component is the use of the abundant and naturally occurring diterpenoids (+)-sclareolide and (+)-sclareol as starting materials, which enables the gram-scale preparation of the key intermediates totarane (1) and s-trans-12E,14-Labdadien-20,8beta-olide (2). Subsequently a thermal or an erbium-catalyzed intermolecular Diels-Alder reaction of totarane (1) with labdadienolide (2) provide convergent and rapid access to the natural product hispidanin A (4).
CONCLUSIONS:
The synthetic studies have offered significant impetus for the efficient construction of these architecturally complex natural products. | | Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(7):628-32. | | Two new labdane diterpenoids from the rhizomes of Isodon yuennanensis.[Pubmed: 25420949 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new labdane diterpenoids, s-trans-8(17),12E,14-labdatrien-20-oic acid (1), s-trans-12E,14-Labdadien-20,8beta-olide (2), along with 10 known compounds, hinokiol (3), ursonic acid (4), 2α,3α-dihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (5), 2α,3β,23-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (6), ethyl 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)lactate (7), ethyl rosmarinate (8), (Z,E)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethenyl caffeic ester (9), tridecanoic acid (10), β-sitosterol (11) and daucosterol (12), were isolated from the 70% acetone extract of the rhizomes of Isodon yuennanensis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Their structures were elucidated based on the analyses of extensive spectroscopic data and physicochemical properties. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)