| Structure Identification: |
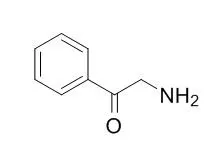
| Org Lett. 2005 Oct 27;7(22):4787-9. | | An advantageous route to oxcarbazepine (trileptal) based on palladium-catalyzed arylations free of transmetallating agents.[Pubmed: 16235889 ] | A new route to oxcarbazepine (Trileptal), the most widely prescribed antiepileptic drug, starting from commercially available 2'-Aminoacetophenone and 1,2-dibromobenzene, is reported.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The sequentially accomplished key steps are palladium-catalyzed intermolecular alpha-arylation of ketone enolates and intramolecular N-arylation reactions. After several experiments to establish the best conditions for both arylation processes, the target oxcarbazepine is obtained in a satisfactory overall yield, minimizing the number of steps and employing scalable catalytic procedures developed in partially aqueous media. | | Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2005 Apr;4(4):367-75. | | Intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen-bonding effects on photophysical properties of 2'-aminoacetophenone and its derivatives in solution.[Pubmed: 15803207] | Effects of intra- and intermolecular hydrogen-bonds on the photophysical properties of 2'-Aminoacetophenone derivatives (X-C6H4-COCH3) having a substituted amino group (X) with different hydrogen-bonding ability to the carbonyl oxygen (X: NH2(AAP), NHCH3(MAAP), N(CH3)2(DMAAP), NHCOCH3(AAAP), NHCOCF3(TFAAP)) are investigated by means of steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy and time-resolved thermal lensing.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Based on the photophysical parameters obtained in aprotic solvents with different polarity and protic solvents with different hydrogen-bonding ability, the characteristic photophysical behavior of the 2'-Aminoacetophenone derivatives is discussed in terms of hydrogen-bonding and n,pi*-pi,pi* vibronic coupling. The dominant deactivation process of AAP and MAAP in nonpolar aprotic solvents is the extremely fast internal conversion (k(ic)= 1.0 x 10(11) s(-1) for AAP and 3.9 x 10(10) s(-1) for MAAP in n-hexane). The internal conversion rates of both compounds decrease markedly with increasing solvent polarity, suggesting that vibronic interactions between close-lying S1(pi,pi*) and S2(n,pi*) states lead to the large increase in the non-radiative decay rate of the lowest excited singlet state. It is also suggested that for MAAP, which has a stronger hydrogen-bond as compared to AAP, an intramolecular hydrogen-bonding induced deactivation is involved in the dissipation of the S1 state.
CONCLUSIONS:
For DMAAP, which cannot possess an intramolecular hydrogen-bond, the primary relaxation mechanism of the S1 state in nonpolar aprotic solvents is the intersystem crossing to the triplet state, whereas in protic solvents very efficient internal conversion due to intermolecular hydrogen-bonding is induced. In contrast, the fluorescence spectra of AAAP and TFAAP, which have an amino group with a much stronger hydrogen-bonding ability, give strongly Stokes-shifted fluorescence, indicating that these compounds undergo excited-state intramolecular proton transfer reaction upon electronic excitation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)