| In vitro: |
| Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2003 Aug;51(8):935-41. | | Diterpenes from the roots of Euphorbia kansui and their in vitro effects on the cell division of Xenopus (part 2).[Pubmed: 12913231] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four new ingenane-type diterpenes, 3-O-(2,3-dimethylbutanoyl)-13-O-dodecanoyl-20-O-acetylingenol (1), 3-O-(2,3-dimethylbutanoyl)-13-O-dodecanoyl-20-Deoxyingenol (2), 3-O-(2E,4Z-decadienoyl)-20-Deoxyingenol (3), and 3-O-(2E,4E-decadienoyl)-20-Deoxyingenol (4), two new jatrophane-type diterpenes, kansuinins D (9) and E (10), and four known ingenane-type diterpenes were isolated from the root of Euphorbia kansui. Their structures were elucidated by spectroscopic and chemical analysis, and individual Xenopus cells at the blastular stage were cultured with the diterpenes to test for biological activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
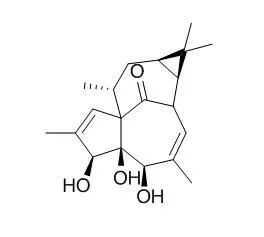
20-Deoxyingenol diterpenes 3 and 4 induced the greatest cell cleavage arrest (0.5 micro g/ml of each compound resulted in >75% cleavage arrest), but cell cleavage inhibitory activity became weak when C-16 had an acyl residue. In contrast, the jatrophane diterpene kansuinin D (9) showed no activity. | | Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, 2016 , 14 (12) :939-945. | | Regio- and stereo-selective hydroxylations of ingenane diterpenoids by Mortierella ramanniana and Gibberella fujikuroi.[Reference: WebLink] | The regio- and stereo-selective hydroxylations of two ingenane diterpenoids, 20-Deoxyingenol (1) and 13-oxyingenol dodecanoat (2), by the filamentous fungi Mortierella ramanniana and Gibberella fujikuroi were investigated in the present study.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four undescribed metabolites (3-6) of substrate 1 and two undescribed metabolites (7 and 8) of substrate 2 were isolated. All the metabolites were identified as hydroxylated ingenane derivatives by extensive NMR and HR-ESI-MS data analyses. All the biotransformed compounds and the substrates were evaluated for their cytotoxicities against three human cancer cell lines, including human colon cancer Caco-2, breast cancer MCF-7, and adriamycin (ADM)-resistant MCF-7/ADM cell lines. All ingenane alcohols (1, and 3-6) displayed no significant cytotoxic activities. The substrate 13-oxyingenol dodecanoat (2) showed moderate cytotoxicity with IC50 values being 35.59 ± 5.37 μmol·L-1 (Caco-2), 24.04 ± 4.70 μmol·L-1 (MCF-7), and 22.24 ± 5.19 μmol·L-1 (MCF-7/ADM). However, metabolites 7 and 8 displayed no significant cytotoxicity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicated that the hydroxylation at the C-13 aliphatic acid ester of substrate 2 can significantly reduce the cytotoxic activity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)