| Description: |
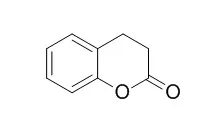
3,4-Dihydrocoumarin is widespread used as a flavoring agent in beverages, gelatins, puddings, candy, and other food items; as a fragrance in perfumes, creams, and cosmetics. |
| In vitro: |
| Herba Polonica, 2010 , 56 (4) :14-9. | | The influence of shading on the yield and quality of southern sweet-grass (Hierochloë australis (Schrad.) Roem. & Schult.) raw material[Reference: WebLink] | Southern sweet-grass (Poaceae) rarely occurs in Polish coniferous or mixed forests. Leaves of this plant, rich in coumarin compounds, are mainly used as a flavouring raw material in alcohol, tobacco and cosmetic industry.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The aim of the study was to investigate the influence of shading on the yield and quality of southern sweet-grass. The experiment was established at the certificated organic field of Department of Vegetable and Medicinal Plants. The sunlight was reduced up to 50 and 70% by using shading nets. The object of experiment was two-year-old plants grown on the alluvial soil. Leaves were harvested two times: in mid-May and in the last week of August (regrowth). The highest yield of leaves was observed at 50% of shading.
CONCLUSIONS:
The shaded plants were characterized by higher content of coumarin and 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin and lower content of bergapten in comparison to non-shaded ones. In the leaves five phenolic acids and two flavonoids were identified. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Natl Toxicol Program Tech Rep Ser. 1993 Sep;423:1-336. | | NTP Toxicology and Carcinogenesis Studies of 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin (CAS No. 119-84-6) in F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice (Gavage Studies).[Pubmed: 12616288] | 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin was nominated by the Food and Drug Administration and the National Cancer Institute for study because of its widespread use as a flavoring agent in beverages, gelatins, puddings, candy, and other food items; as a fragrance in perfumes, creams, and cosmetics; and because of interest in the structure-activity relationships of the coumarin derivatives.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Toxicity and carcinogenicity studies were conducted by administering 3,4-Dihydrocoumarin (99% pure) in corn oil by gavage to groups of male and female F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice for 16 days, 13 weeks, and 2 years. Genetic toxicology studies were conducted in Salmonella typhimurium, cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells, and peripheral blood cells of mice. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)