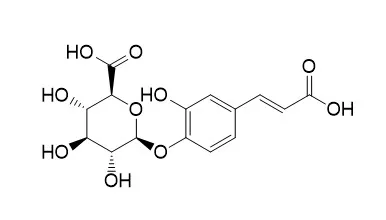
| Stauntonia hexaphylla leaf extract (YRA-1909), which is widely used for the antirheumatic properties, has been under phase 2 clinical trials in patients with rheumatoid arthritis since April 2017. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method while using liquid⁻liquid extraction with ethyl acetate was validated for the simultaneous determination of the major active components of YRA-1909, including chlorogenic acid (CGA), neochlorogenic acid (NCGA), cryptochlorogenic acid (CCGA), and their metabolites (i.e., caffeic acid (CA), caffeic acid 3-O-glucuronide (CA-3-G), Caffeic acid 4-O-glucuronide (CA-4-G), and ferulic acid (FA)) in rat plasma and applied to a pharmacokinetic study of YRA-1909 in rats. Seven analytes were separated on Halo C18 while using gradient elution of formic acid and methanol, and then quantified in selected reaction monitoring mode whle using negative electrospray ionization. Following oral administration of YRA-1909 at doses of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg to male Sprague-Dawley rats, CGA, NCGA, and CCGA were rapidly absorbed and metabolized to CA, CA-3-G, and CA-4-G. The area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUClast) of CGA, NCGA, CCGA, and three metabolites linearly increased as the YRA-1909 dose increased. Other pharmacokinetic parameters were comparable among three doses studied. AUClast values for CA, CA-3-G, and CA-4-G exceeded those for CGA, NCGA, and CCGA. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)