| Kinase Assay: |
| Nat Prod Res. 2008;22(16):1441-50. | | Apoptotic cell death through inhibition of protein kinase CKII activity by 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde purified from Xanthium strumarium.[Pubmed: 19023807] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
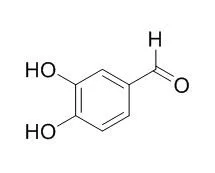
The CKII inhibitory compound was purified from the fruit of Xanthium strumarium by organic solvent extraction and silica gel chromatography. The inhibitory compound was identified as 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde by analysis with FT-IR, FAB-Mass, EI-Mass, (1)H-NMR and (13)C-NMR. 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde inhibited the phosphotransferase activity of CKII with IC(50) of about 783 microM. Steady-state studies revealed that the inhibitor acts as a competitive inhibitor with respect to the substrate ATP. A value of 138.6 microM was obtained for the apparent K(i). Concentration of 300 microM 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde caused 50% growth inhibition of human cancer cell U937. 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde-induced cell death was characterised with the cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and procaspase-3. Furthermore, the inhibitor induced the fragmentation of DNA into multiples of 180 bp, indicating that it triggered apoptosis. This induction of apoptosis by 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde was also confirmed by using flow cytometry analysis.
CONCLUSIONS:
Since CKII is involved in cell proliferation and oncogenesis, these results suggest that 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde may function by inhibiting oncogenic disease, at least in part, through the inhibition of CKII activity. |
|
| Cell Research: |
| Phytomedicine. 2009 Jan;16(1):85-94. | | 3,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde purified from the barley seeds (Hordeum vulgare) inhibits oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis via its antioxidant activity.[Pubmed: 19022639] | Barley is a major crop worldwide. It has been reported that barley seeds have an effect on scavenging ROS. However, little has been known about the functional role of the barley on the inhibition of DNA damage and apoptosis by ROS.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, we purified 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde from the barley with silica gel column chromatography and HPLC and then identified it by GC/MS. And we firstly investigated the inhibitory effects of 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde purified from the barley on oxidative DNA damage and apoptosis induced by H(2)O(2), the major mediator of oxidative stress and a potent mutagen. In antioxidant activity assay such as DPPH radical and hydroxyl radical scavenging assay, Fe(2+) chelating assay, and intracellular ROS scavenging assay by DCF-DA, 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde was found to scavenge DPPH radical, hydroxyl radical and intracellular ROS. Also it chelated Fe(2+). In in vitro oxidative DNA damage assay and the expression level of phospho-H2A.X, it inhibited oxidative DNA damage and its treatment decreased the expression level of phospho-H2A.X. And in oxidative cell death and apoptosis assay via MTT assay and Hoechst 33342 staining, respectively, the treatment of 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde attenuated H(2)O(2)-induced cell death and apoptosis.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the barley may exert the inhibitory effect on H(2)O(2)-induced tumor development by blocking H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative DNA damage, cell death and apoptosis. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| The Korea Jounnal of Herbology, 2006, 21(2):1-7. | | Tyronase Inhibitory Effect of 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde Isolated from Pinellia ternata.[Reference: WebLink] | The purpose of this study is to isolate tyrosinase inhibitory material from Pinellia ternata and characterize its own structure and activity.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Pinellia ternata (600g) was extracted with 95% methanol (1L) at for 4 days, with shaking at 250rpm. The extract was further solvent-fractionated with n-hexane, chloroform, ethylacetate and water. The active fraction was subjected to JAI recycling prep-HPLC JAIGEL GS-320 column. The structure was identified for the active peak with NMR and GC. Results : Tyrosinase was potently inhibited by 95% methanol extracts from Pinellia ternata. The IC(50) value of the extracts was estimated to be 0.05mg/ml. The extracts was divided into four solvent-fractions, and the most potent tyrosinase inhibition was found in ethylacetate layer. IC(50) value of ethylacetate fraction was 0.001mg/ml. This fraction was further purified with JAI Recycling Preparative HPLC (Model: LC 9104). The isolated compound showing inhibitory activity was characterized on its chemical structure by NMR and the compound was identified as 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde. IC(50) was found to be 7.74 which is much lower than that of kojic acid .
CONCLUSIONS:
The data suggest that 3,4-Dihydroxybenzaldehyde isolated and identified from Pinellia ternata is very strong inhibitor to melanin biosynthesis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)