| Structure Identification: |
| Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society, 1999, 46(1):77-86. | | Cheritamine, A New N‐Fatty Acyl Tryptamine and Other Constituents from the Stems of Annona cherimola.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
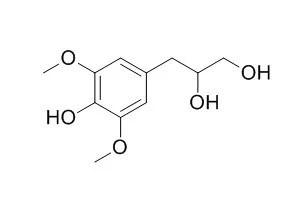
A new N‐fatty acyl tryptamine, cheritamine (30), along with thirty‐two compounds including nineteen benzenoids, p‐hydroxybenzadehyde (1), p‐hydroxybenzoic acid (2), methylparabene (3), 3‐chlorobenzoic acid (4), vanillin (5), isovanillin (6), vanillic acid (7), isovanillic acid (8), methyl vanillate (9), methyl isovanillate (10), syringaldehyde (11), syringic acid (12), 3,4,5‐trimethoxybenzoic acid (13), trans‐methyl p‐coumarate (14), ferulic acid (15), p‐dihydrocoumaric acid (16), 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1,2-propanediol (17), 3,4,5‐trimethoxyphenyl‐β‐D‐glucopyranoside (18) and thalictoside (19); one p‐quinone, 2,6‐dimethoxy‐p‐quinone (20); one purine, uridine (21); eight alkaloids, nicotinic acid (22), thalifoline (23), doryphornine (24), (–)‐norstephalagine (25), (‐)‐romucosine (26), (+)‐pronuciferine (27), (+)‐norisocorydine (28) and oxoasimilobine (29) and three steroids, β‐sitosterol‐D‐glucoside (31), stigmasterol‐D‐glucoside (32) and 6′‐(β‐sitosteryl‐3‐O‐β‐glucopyranosidyl)hexadecanoate (33), are isolated from the stems of Annona cherimola.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds were characterized and identified by physical and spectral evidence. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)