| In vivo: |
| Journal of Pharmacology & Experimental Therapeutics, 2012, 341(3):794-801. | | 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid, a specific agonist for hydroxycarboxylic acid 1, inhibits lipolysis in adipocytes.[Reference: WebLink] | Niacin raises high-density lipoprotein and lowers low-density lipoprotein through the activation of the β-hydroxybutyrate receptor hydroxycarboxylic acid 2 (HCA2) (aka GPR109a) but with an unwanted side effect of cutaneous flushing caused by vascular dilation because of the stimulation of HCA2 receptors in Langerhans cells in skin. HCA1 (aka GPR81), predominantly expressed in adipocytes, was recently identified as a receptor for lactate. Activation of HCA1 in adipocytes by lactate results in the inhibition of lipolysis, suggesting that agonists for HCA1 may be useful for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Lactate is a metabolite of glucose, suggesting that HCA1 may also be involved in the regulation of glucose metabolism. The low potency of lactate to activate HCA1, coupled with its fast turnover rate in vivo, render it an inadequate tool for studying the biological role of lactate/HCA1 in vivo.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
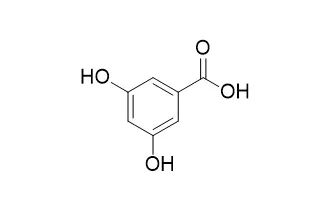
In this article, we demonstrate the identification of 3-hydroxybenzoic acid (3-HBA) as an agonist for both HCA2 and HCA1, whereas 3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (3,5-DHBA) is a specific agonist for only HCA1 (EC(50) ∼150 μM). 3,5-DHBA inhibits lipolysis in wild-type mouse adipocytes but not in HCA1-deficient adipocytes.
CONCLUSIONS:
Therefore, 3,5-DHBA is a useful tool for the in vivo study of HCA1 function and offers a base for further HCA1 agonist design. Because 3-HBA and 3,5-DHBA are polyphenolic acids found in many natural products, such as fruits, berries, and coffee, it is intriguing to speculate that other heretofore undiscovered natural substances may have therapeutic benefits. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)