| Structure Identification: |
| Pharmaceutical Biology, 2008, 22(1):1-10. | | Lipids and Saponins of Phaseolus coccineus.[Reference: WebLink] | The lipids obtained from the roots, rhizomes and stems of Phaseolus coccineus were separated into saponifiable and unsaponifiable fractions.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
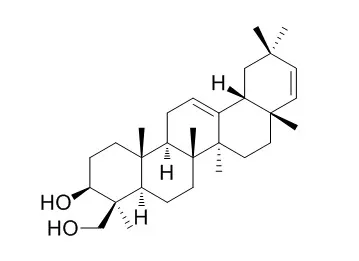
Analysis of the saponifiable fraction by gas-liquid chromatography (GLC) of the methyl esters showed the presence of a series of C8 to C18 saturated acids and C12 to C18 unsaturated acids. Oleic acid was the predominant fatty acid detected in the roots (22.3%) and rhizomes (34.4%). However, in the stems palmitic acid (30.0%) was the major component. Stearic acid, which was present in a fairly high concentration in the rhizomes, was not detected in either the roots or the stems. β-Bergamotane, 18α-oleanan-3-one and β-Sitosterol have been isolated from the roots, rhizomes and stems of unsaponifiable fraction. In all these three plant materials, the presence of saponins was also revealed. Two sapogenins were isolated from the roots and were identified as Soyasapogenol C and Ursa-12,15-diene-3,24-diol. Soyasapogenol C was also isolated from the rhizomes and the stems. In addition, soyasapogenol B was also isolated and identified in the stems.
CONCLUSIONS:
The compounds were identified by TLC, UV, IR, NMR and mass spectral methods. The sugar moieties associated with these sapogenins were identified as D-glucose, D-fructose, L(+)-arabinose, L(+)-rhamnose and D-galacturonic acid. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)