| Description: |
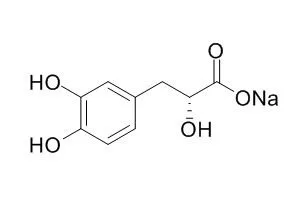
Sodium danshensu (SDSS), the sodium salt of danshensu (DSS), has the neuroprotective effect against cerebral I/R injury, and the potential mechanism might to inhibition of apoptosis through activating the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. SDSS has a protective effect against the genotoxicity of cigarette smoke,it shows a biphasic effects on vessel tension, while low dosage of sodium danshensu produces small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca(2+) influx, high dosage produces significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K(+) channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells. |
| Targets: |
Calcium Channel | Potassium Channel | Akt | GSK-3 | Bcl-2/Bax | PI3K |
| In vitro: |
| Drugs & Clinic, 2014, 29(1):21-6. | | Protection of flavonoid components baicalein,quercetin,or sodium danshensu on cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage induced by cigarette smoke[Reference: WebLink] | | To evaluate the protective effect of flavonoid components baicalein, quercetin or Sodium Danshensu on cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage induced by cigarette smoke. Methods Two kinds of eukaryotic cells B-16 cells and oral buccal mucosal cells in liquid were attacked by the mainstream smoke produced via on-line cigarette smoking according to FTC with or without baicalein, quercetin or Sodium Danshensu. The cytotoxicity and cellular DNA damage were respectively assessed by MTT method and single cell gel electrophoresis. Results The cytotoxicity of B-16 cells and DNA damage of two kinds of cells induced by on-line cigarette smoking were obvious. A positive relationship was observed between the exposure time in smoke and the tail moment and olive tail moment of comet cells. Baicalein, quercetin, or Sodium Danshensu(1 mmol/L) could relieve the cytotoxicity by about 50% and decrease the DNA damage by more than 60%. Conclusion There is a positive relationship between the exposure of cells in smoke and the cellular DNA damage, and the flavonoid components baicalein, quercetin, or Sodium Danshensu have a protective effect against the genotoxicity of cigarette smoke. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010 Apr;31(4):421-8. | | Biphasic effects of sodium danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aorta.[Pubmed: 20228827] | To investigate the effects of Sodium Danshensu on vessel function in isolated rat aortic ring.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Thoracic aortae from normal rats were isolated and equilibrated in organ bath with Krebs-Henseleit buffer and ring tension was recorded. Effects of Sodium Danshensu on basal tonus of the vessel and its effects on vessel contraction and relaxation with or without endothelium were observed.
In thoracic arteries under basal tonus, Sodium Danshensu (0.3-3 g/L) produced a dose-dependent transient contraction. In phenylephrine-precontracted thoracic arteries with or without endothelium, low concentration (0.1-0.3 g/L) of Sodium Danshensu produced a weak contraction, while high concentrations (1-3 g/L) produced a pronounced vasodilator after a transient vasocontraction. Pre-incubation with Sodium Danshensu could inhibit vessel contraction induced by phenylephrine and potassium chloride in a concentration-dependent way. Sodium Danshensu inhibited phenylephrine- and CaCl(2)-induced vasoconstriction in Ca(2+)-free medium. Pre-incubation with tetraethylammonium, a non-selective K(+) channel blocker, and apamin, a small-conductance calcium-activated K(+) channel blocker partially antagonized the relaxation response induced by Sodium Danshensu. However, iberiotoxin (big-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channel blocker), barium chloride (inward rectifier K(+) channel blocker), and glibencalmide (ATP-sensitive K(+) channel blocker) had no influence on the vasodilation effect of Sodium Danshensu.
CONCLUSIONS:
Sodium Danshensu showed a biphasic effects on vessel tension. While low dosage of Sodium Danshensu produced small contraction possibly through transient enhancement of Ca(2+) influx, high dosage produced significant vasodilation mainly through promoting the opening of non-selective K(+) channels and small-conductance calcium-sensitive K(+) channels in the vascular smooth muscle cells. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)