| In vitro: |
| Food Science and Technology International, Tokyo.2003 May 1;9(2):197-201. | | Antioxidative, Antihyaluronidase and Antityrosinase Activities of Some Constituents from the Aerial Part of Piper elongatum VAHL.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
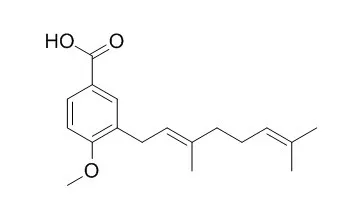
The scavenging effects on 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), the antihyaluronidase and the antityrosinase activities of 1–4, asebogenin (8), 2′,6′-dihydroxy-4′-methoxydihydrochalcone (9), 3-Geranyl-4-methoxybenzoic acid (10), 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (11), nervogenic acid (12) and 2,2-dimethyl-6-carboxyl-8-prenyl-chromene (13), which were previously isolated from the MeOH extract were evaluated.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 4, 8 and 9 showed higher radical scavenging effect than that of L-cysteine, and 4, 8 and 11 exhibited stronger inhibition effect on the activation of hyaluronidase than that of tranilast. Compound 8 indicated almost the same antityrosinase activity as that of kojic acid. | | Food Science and Technology Research.1997;3(3):285-289. | | Antioxidative Constituents from the Aerial Part of Piper elongatum VAHL.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Six aromatic compounds, asebogenin (1), 2',6'-dihydroxy-4'-methoxydihydrochalcone (2), 3-Geranyl-4-methoxybenzoic acid (3), 3-geranyl-4-hydroxybenzoic acid (4), nervogenic acid (5) and 2,2-dimethyl-6-carboxyl-8-prenyl-chromene (6) were isolated from the methanol extract of the aerial part of Piper elongatum VAHL., whose leaves are used as a folk medicine in South America. The structures of 1-6 were elucidated by MS, 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectroscopies, and chemical evidence.
CONCLUSIONS:
Among these compounds, 1 showed stronger antioxidative activity than that of α-tocopherol, and 4 and 5 exhibited higher activity than that of t-butyl-4-hydroxyanisole (BHA) using the ferric thiocyanate method. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)