| In vitro: |
| Pmio, 2016, 3(03):e64-e67. | | In Vitro Mammalian Arginase Inhibitory and Antioxidant Effects of Amide Derivatives Isolated from the Hempseed Cakes (Cannabis sativa).[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
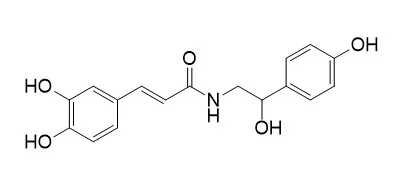
In an effort to identify novel inhibitors of arginase, a phytochemical study was performed on hempseed cakes (Cannabis sativa L.). It led to the isolation of a new lignanamide, cannabisin I ( 1), together with seven known lignanamides, cannabisins A, B, C, F, M, 3,3′-demethylgrossamide, grossamide, and two phenylpropanoid amides, N-trans-caffeoyltyramine and N-trans-caffeoyloctopamine, among which was later identified for the first time from C. sativa. Their structures were elucidated by comprehensive analysis of NMR spectroscopy and mass spectrometry data. These compounds were evaluated on mammal arginase (purified liver bovine arginase), showing that N-trans-caffeoyltyramine exhibited the higher activity with an IC50 value of 20.9 µM, which remains, however, less active than the reference compound S-(2-boronoethyl)-l-cysteine (IC50 = 4.3 µM). Radical scavenging capacity of these compounds was determined by the ORAC-FL method.
CONCLUSIONS:
All tested cannabisins displayed antioxidant activity close to or better than the reference compounds. N-trans-Caffeoyltyramine has both arginase inhibitory property and antioxidant capacity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)