| Description: |
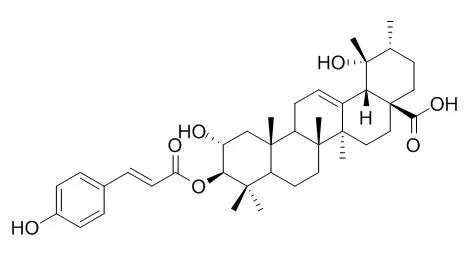
3-O-(E)-p-coumaroyl tormentic acid may be promising lead compound for developing an effective drug for treatment of leukemia, it induces apoptotic cell death in human leukemia (HL60) via mainly mitochondrial pathway by, at least in part, Topo I inhibition. 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid shows cytotoxicity against four human tumor cell lines (A549, SK-OV-3, SK-MEL-2, and HCT-15) in vitro, the IC50 values of 13.72, 14.29,14.61, 14.04 uM, respectively. 3beta-O-cis-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid, and 3beta-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid are weakly selective for vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE) compared with eukaryotic cells, with an MIC of 59.4microg/mL and a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 72.0microg/mL for monkey kidney epithelial (MA104) cells. A mixture of 3-O-cis-p-coumaroyltormentic acid and 3-O-trans-p-coumaroyltormentic acid shows an inhibitory effect comparable to (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) of green tea on the activation of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) induced by 12-O-tetradeca--noylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA).
|
| In vitro: |
| Phytochemistry. 2002 Feb;59(3):315-23. | | Production of bioactive triterpenes by Eriobotrya japonica calli.[Pubmed: 11830140 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Callus tissue cultures induced from an axenic leaf of Eriobotrya japonica (Rosaceae) produced triterpenes in large amounts (ca. 50 mg/g dry wt). Nine triterpenes were characterized as ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, 2alpha-hydoxyursolic acid, maslinic acid, tormentic acid, 2alpha, 19alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid, hyptadienic acid and a mixture of 3-O-cis-p-coumaroyltormentic acid and 3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid. The triterpene composition in the callus tissues was noticeably different from that in intact leaves. The contents of tormentic acid with antidiabetic action, and 2alpha, 19alpha-dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid with anti-HIV activity, were much larger than those in the intact leaves.
CONCLUSIONS:
All of the triterpenes isolated from the callus tissues showed an inhibitory effect comparable to (-)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) of green tea on the activation of Epstein-Barr virus early antigen (EBV-EA) induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA). 2alpha, 19alpha-Dihydroxy-3-oxo-urs-12-en-28-oic acid was the most potent inhibitor among them and caused a significant delay of two-stage carcinogenesis on mouse skin. | | Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2011;59(3):378-81. | | 3-O-(E)-p-coumaroyl tormentic acid from Eriobotrya japonica leaves induces caspase-dependent apoptotic cell death in human leukemia cell line.[Pubmed: 21372421] | Eleven triterpene acids, 1-11, isolated from the leaves of Eriobotrya japonica, were evaluated for inhibition of DNA topoisomerase (Topo) I and cytotoxicity against human leukemia (HL60) and melanoma cell lines (CRL1579).
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Among the compounds tested, four compounds, δ-oleanolic acid (4), ursolic acid (5), 3-O-(E)-p-coumaroyl tormentic acid (3-O-trans-p-Coumaroyltormentic acid,8), and betulinic acid (10), exhibited potent Topo I inhibitory activity (IC(50) 20.3-36.5 μM) and cytotoxicity against HL60 (EC(50) 5.0-8.1 μM). Upon assessing the apoptosis-inducing activity in HL60 cells, compound 8 exhibited induction of apoptosis detected by the observation of DNA fragmentation and membrane phospholipid exposure in flow cytometry. Western blot analysis showed that compound 8 markedly reduced the levels of procaspases-3 and 9, while being increased the levels of cleaved caspases-3 and 9. On the other hand, compound 8 exerted almost no influence on the expression of caspase-8. In addition, compound 8 increased significantly Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and activated caspase-2.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggested that compound 8 induced apoptotic cell death in HL60 via mainly mitochondrial pathway by, at least in part, Topo I inhibition. Therefore, compound 8 may be promising lead compound for developing an effective drug for treatment of leukemia. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)