| In vitro: |
| Planta Medica, 2000, 66(8):768-769. | | Antimicrobial triterpenoids from Licania heteromorpha.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
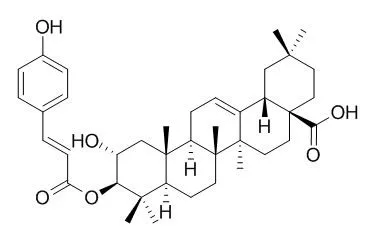
Six triterpenoids having a lupane and oleane skeleton were isolated from the leaves and young branches of Licania heteromorpha Bentham var. heteromorpha and were identified as: betulinic acid 1, alphitolic acid 2, 3 beta-O-trans-p-coumaroyl alphitolic acid 3,
3 beta-O-cis-p-coumaroyl alphitolic acid 4, 3-beta-O-(trans-p-Coumaroyl)maslinic acid 5, 3 beta-O-cis-p-coumaroyl maslinic acid 6. The antimicrobial activity of these compounds was evaluated in vitro on clinically isolated microorganisms employing a microdilution method.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 2, 3, 5, and 6 showed antimicrobial activity on Gram-positive bacteria and yeasts, whereas none of the six triterpenoids were active against Gram-negative organisms. | | Journal of Natural Products, 1999, 62(12):1660-1663. | | DNA polymerase beta inhibitors from Tetracera boiviniana.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bioassay-guided fractionation of an active methyl ethyl ketone extract of Tetracera boiviniana, using a sensitive assay to monitor DNA polymerase beta inhibition, resulted in the isolation of three known triterpenoids, betulinic acid (1), 3-cis-p-coumaroyl maslinic acid (2), and 3-beta-O-(trans-p-Coumaroyl)maslinic acid (3).
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1-3 inhibited DNA polymerase beta with IC50 values of 14, 15, and 4.2 microM in the presence of bovine serum albumin (BSA) and 6.5, 7.5, and 2.0 microM in the absence of BSA, respectively. Further, compounds 1-3 potentiated the effects of bleomycin in cultured P-388D1 cells. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)