| In vitro: |
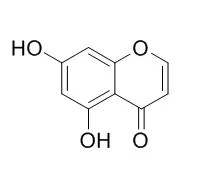
| Life Sci. 2015 Jun 1;130:25-30. | | Neuroprotection against 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells by 5,7-Dihydroxychromone: Activation of the Nrf2/ARE pathway.[Pubmed: 25818191] | The aim of this study was to prove the neuroprotective effect of 5,7-Dihydroxychromone (DHC) through the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. To elucidate the mechanism, we investigated whether 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells could be attenuated by DHC via activating the Nrf2/ARE signal and whether 5,7-Dihydroxychromone could down-regulate 6-OHDA-induced excessive ROS generation
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To evaluate the neuroprotective effect of 5,7-Dihydroxychromone against 6-OHDA-induced apoptosis, FACS analysis was performed using PI staining. The inhibitory effect of 5,7-Dihydroxychromone against 6-OHDA-induced ROS generation was evaluated by DCFH-DA staining assay. Additionally, translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus and increased Nrf2/ARE binding activity, which subsequently resulted in the up-regulation of the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant gene expressions including HO-1, NQO1, and GCLc, were evaluated by Western blotting and EMSA.Pre-treatment of 5,7-Dihydroxychromone, one of the constituents of Cudrania tricuspidata, significantly protects 6-OHDA-induced neuronal cell death and ROS generation. Also, DHC inhibited the expression of activated caspase-3 and caspase-9 and cleaved PARP in 6-OHDA-induced SH-SY5Y cells. 5,7-Dihydroxychromone induced the translocation of Nrf2 to the nucleus and increased Nrf2/ARE binding activity which results in the up-regulation of the expression of Nrf2-dependent antioxidant genes, including HO-1, NQO1, and GCLc. The addition of Nrf2 siRNA abolished the neuroprotective effect of DHC against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity and the expression of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant genes.
CONCLUSIONS:
Activation of Nrf2/ARE signal by 5,7-Dihydroxychromone exerted neuroprotective effects against 6-OHDA-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis. This finding will give an insight that activating Nrf2/ARE signal could be a new potential therapeutic strategy for neurodegenerative disease. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2014;78(8):1392-401. | | Anti-diabetic properties of Daphniphyllum macropodum fruit and its active compound.[Pubmed: 25130743] | Among the compounds isolated, 5,7-Dihydroxychromone potently induced the differentiation of mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. DME and 5,7-Dihydroxychromone increased PPARγ and liver X receptor α (LXRα) mRNA expression levels.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To determine whether the adipogenic effects we observed might affect serum glucose levels, we undertook in vivo experiment using streptozotocin-/high-fat diet-induced type 2 diabetes mouse model. DME supplementation reduced serum glucose, total cholesterol, and triacylglycerol levels in diabetes mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that DME may be useful for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Moreover, it was proposed that 5,7-Dihydroxychromone isolated from DME is one of the active compounds that may contribute to regulate blood glucose levels. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)