METHODS AND RESULTS:
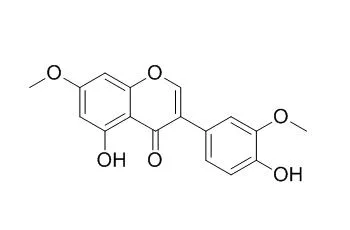
The chemical study of the extracts from leaves and stems of Ouratea ferruginea allowed the identification of a new isoflavone, 5-hydroxy-7,3'4'5'-tetramethoxyisoflavone, and twenty two known compounds, including friedelin, 3β-friedelinol, lupeone, a mixture of sitosterol, stigmasterol and campesterol, sitosteryl- and stigmasteryl-3-O-b-D-glucopyranosides, 5,4'-dihydroxy-7,5',3'-trimethoxyisoflavone, 5,4'-dihydroxy-7,3'-di-methoxyisoflavone (7,3'-Di-O-methylorobol), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3',5'-dimethoxyisoflavone (piscigenin), 2R,3R-epicatechin, syringic acid, 2,6-dimethoxybenzoquinone, 2,6-dimethoxyhydroquinone, syringic and ferulic aldehyde, a mixture of vanillic acid, 1-hydroxy-2-methoxy-4-(1E-3-hydroxy-1-propenyl)-benzene and 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy-dihydrocinamaldehyde, besides amenthoflavone and 7-O-methylamenthoflavone (sequoiaflavone) which are considered as chemotaxonomic markers of Ouratea. The structures were identified by IR, (1)H- and (13)C-NMR and GC-MS, HPLC-MS, besides comparison with literature data. The inhibitory effects of 5,4'-dihydroxy-7,5',3'-trimethoxyisoflavone, 7,3'-Di-O-methylorobol, piscigenin and 7-O-methylamenthoflavone on cytochrome P450-dependent 7-ethoxycoumarin O-deethylase (ECOD) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) were evaluated in vitro.
CONCLUSIONS:
The 5,4'-dihydroxy-7,5',3'-trimethoxy-isoflavone was the best inhibitor, inhibiting almost 75% of GST activity. Sequoiaflavone was the most potent inhibitor, inhibiting ECOD assay in 75%. These activities allow us to consider both these flavonoids as potential anticancer and chemopreventive agents. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)