| Structure Identification: |
| Phytochemistry,1992,31(10): 3659–3661. | | Lignans from leaves of Juniperus chinensis[Reference: WebLink] | Umbelliferone, 13 lignans and an unusual compound 2-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)propane-1,3-diol, were isolated from the leaves of Juniperus chinensis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
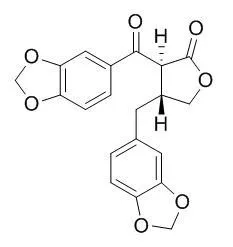
The lignans include meso-secoisolariciresinol, 3,4-methylenedioxy-3′,4′-dimethoxylignan-9′,9-olide, hibalactone, isohibalactone, 7-Oxohinokinin, 7-hydroxyhinokinin, 7-acetyloxyhinokinin, (+)-xanthoxylol, dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol, 3-methoxy-8,4′-oxyneoligna-3′,4,7,9,9′-pentol and three new compounds, viz., (8S)-3-methoxy-8,4′-oxyneoligna-3′,4,9,9′-tetraol, (7S,8S)-3-methoxy-3′,7-epoxy-8,4′-oxyneoligna-4,9,9′-triol and the corresponding (7R,8S)-isomer. | | Journal of Wood Science,2001,47(6): 476-482. | | Lignans ofChamaecyparis obtusa[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Eleven lignans — xanthoxylol (1), 7-Oxohinokinin (2), savinin (3), dihydrosesamin (4), isoactifolin (5), sesamin (6), piperitol (7), hinokinin (8), pluviatolide (9), haplomyrfolin (10), and rnatairesinol (11) — were isolated from young shoots ofChamaecyparis obtusa cv. Breviramea.
CONCLUSIONS:
Eight lignans (1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 9,10, and11) were isolated from this plant for the first time. Chiral high-performance liquid Chromatographie analysis showed that8, 9, 10, and11, were found to be levorotatory and optically pure (>99% e.e.). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)