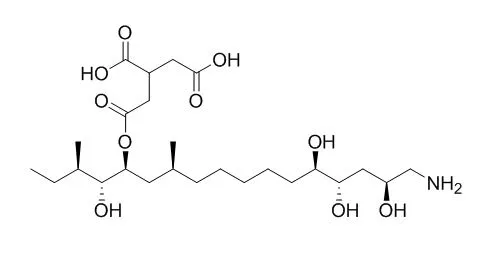
| Structure Identification: |
| Symposium on the Chemistry of Natural Products, symposium papers, 1996(38):631-6. | | The Absolute Configuration of Host-specific Toxin, AAL-toxin TA and Its Synthetic Study[Reference: WebLink] | AAL Toxin TA1(1)and AALtoxin TA2(2)are host-specific toxins (HST) produced by Altemaria altemata f. sp. lycopersici, a causal fungus of tomato stem canker. For understanding the mechanism of the host-specificity of AAL-toxins in molecular level, the elucidation of the stereostructure and synthetic studies are essential.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In order to determine the absolute configuration, 1 and 2 were degraded to 2-methylbutanol, 3-methylnonan-1,9-diol and N-protected 4-amino-butan-1,3-diol, which were further converted to (R)-MTPA esters, These esters were correlated with synthetic samples by comparison of their 500MHz ^1H-NMR spectra. The remaining stereocenters were determined by the comparison of ^1H-NMR spectra of 6a and 6c derived from 1 and 2 with those of synthetic model compounds. These data concluded that AAL-toxins possess 2S, 4S, 5S, 11S, 13S, 14R and 15R configurations. To the syntheses of two vicinal anti-diol moieties in key intermediates of AAL-toxins, asymmetric dihydroxylation has been applied.
CONCLUSIONS:
The strategy allowed efficient construction of left- and right segments of AAL-toxin main chain. Enzymatic resolution of benzylsuccinate ester provided both enantiomers (R)-39 and (S)-40 which were converted to the corresponding tricarballylic acids. Effective couplings of each segment were also investigated. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)