| Description: |
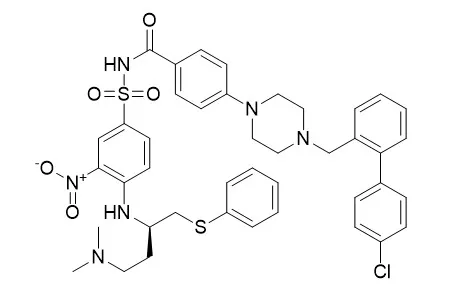
ABT-737 is a BH3 mimetic inhibitor of Bcl-xL, Bcl-2 and Bcl-w with EC50 of 78.7 nM, 30.3 nM and 197.8 nM in cell-free assays, respectively; no inhibition observed against Mcl-1, Bcl-B or Bfl-1. ABT-737 induces mitochondrial pathway apoptosis and mitophagy. |
| Targets: |
Bcl-xL/Bcl-2/Bcl-w |
| In vitro: |
| Cancer Cell,2006 Nov;10(5):389-99. | | The BH3 mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized.[Pubmed: 17097561] | Since apoptosis is impaired in malignant cells overexpressing prosurvival Bcl-2 proteins, drugs mimicking their natural antagonists, BH3-only proteins, might overcome chemoresistance.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Of seven putative BH3 mimetics tested, only ABT-737 triggered Bax/Bak-mediated apoptosis. Despite its high affinity for Bcl-2, Bcl-x(L), and Bcl-w, many cell types proved refractory to ABT-737. We show that this resistance reflects ABT-737's inability to target another prosurvival relative, Mcl-1. Downregulation of Mcl-1 by several strategies conferred sensitivity to ABT-737. Furthermore, enforced Mcl-1 expression in a mouse lymphoma model conferred resistance. In contrast, cells overexpressing Bcl-2 remained highly sensitive to ABT-737.
CONCLUSIONS:
Hence, ABT-737 should prove efficacious in tumors with low Mcl-1 levels, or when combined with agents that inactivate Mcl-1, even to treat those tumors that overexpress Bcl-2. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Cancer Lett,2012 Apr 28;317(2):218-25. | | Targeting Bcl-2 family proteins in adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma: in vitro and in vivo effects of the novel Bcl-2 family inhibitor ABT-737.[Pubmed: 22138435] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATLL) is a peripheral T-cell malignancy caused by human T-lymphotropic virus type I (HTLV-1). ABT-737, a small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Bcl-w, significantly induced apoptosis in HTLV-1 infected T-cell lines as well as in fresh ATLL cells, and synergistically enhanced the cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by conventional cytotoxic drugs. Moreover, ABT-737 significantly inhibited the in vivo tumor growth of an ATLL mouse model.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that the use of an agent targeting anti-apoptotic bcl-2 family proteins, either alone or in combination with other conventional drugs, represents a novel promising approach for ATLL. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)