| Cell Research: |
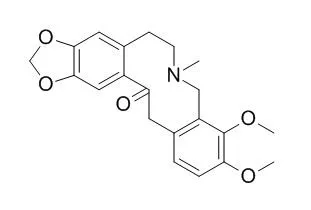
| Toxicol Lett. 2011 Jun 10;203(2):135-41. | | Protopine and allocryptopine increase mRNA levels of cytochromes P450 1A in human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells independently of AhR.[Pubmed: 21419197] | The isoquinoline alkaloids protopine and Allocryptopine are present in phytopreparations from medicinal plants, such as Fumaria officinalis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Since nothing is known about effects of the alkaloids on the expression of xenobiotic-metabolizing enzymes, we examined whether protopine or Allocryptopine affect the expression of cytochromes P450 (CYPs) 1A1 and 1A2 in primary cultures of human hepatocytes and human hepatoma HepG2 cells. In HepG2 cells, protopine and Allocryptopine significantly increased CYP1A1 mRNA levels after 24h exposure at concentrations from 25 and 10 μM, respectively, as shown by real-time PCR. Both protopine and Allocryptopine also dose-dependently increased CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 mRNA levels in human hepatocytes. However, the effects of the tested alkaloids on both cell models were much lower than the effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), a prototypical CYP1A inducer. Using gene reporter assays performed in transiently transfected HepG2 cells, we demonstrated that the induction of CYP1A1 expression by either protopine or Allocryptopine was associated with mild or negligible activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. In contrast to TCDD, CYP1A mRNA levels induced by protopine or Allocryptopine in both HepG2 cells and human hepatocytes did not result in elevated CYP1A protein or activity levels as shown by western blotting and EROD assays, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
We conclude that the use of products containing protopine and/or Allocryptopine may be considered safe in terms of possible induction of CYP1A enzymes. |
|
| Animal Research: |
| Chinese Traditional & Herbal Drugs, 2011, 42(6):1158- 63. | | Effect of allocryptopine on antagonizing hepatic fibrosis.[Reference: WebLink] |
To investigate the prophylactic and therapeutic effects of Allocryptopine on experimental hepatic fibrosis.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Experimental hepatic fibrosis models were induced by injection of tetrachloride in combination with the drinking of 5% alcohol to rats and Schistosoma japomicum infection to mice. The effects of Allocryptopine anti-hepatic fibrosis were evaluated by comparing the liver and spleen indexes, tissue biochemical indices (ALT, AST), lipid peroxidation indices (GSH-Px, MDA, SOD), serum fibrosis indices (HA, PCIII LN), the expression level of Hyp and collagen type I, III (CoI, CoIII), and the liver pathology before and after Allocryptopine intervention. In CCl 4-induced liver fibrosis model rats, compared with model group, the liver index and the expression level of CoI were obviously decreased in Allocryptopine prophylactic groups (P<0.05, 0.01), high-dose prophylactic Allocryptopine could significantly reduce the expression level of CoIII (P<0.01), middle-dose prophylactic Allocryptopine could obviously reduce the spleen index, the content of AST (P<0.05); in Allocryptopine therapeutic group, the liver index, the content of ALT, and the expression level of CoIII were significantly decreased (P<0.05, 0.01). In S. japomicum-induced liver fibrosis model mice, prophylactic Allocryptopine could reduce the content of ALT and the expression level of Hyp (P<0.05); the liver index, the contents of PCIII, HA, and ALT were significantly decreased in high-dose Allocryptopine therapeutic group (P<0.05, 0.01), the liver index, the contents of PCIII, and HA were obviously decreased in middle-dose Allocryptopine therapeutic group (P<0.05); In addition, the hepatic histopathology was also improved in varying degrees after Allocryptopine intervention.
CONCLUSIONS:
Allocryptopine has certain effects on anti-injury for hepatocyte, ameliorating liver function, and prohibiting hepatic fibrosis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)