| Description: |
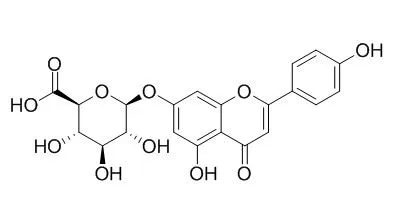
Apigenin-7-glucuronide possesses multiple pharmacological activities, including anti-oxidant, anti-complement, anti-inflammatory, and aldose reductase inhibitory activities, it can inhibit Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP) activities, with IC50s of 12.87, 22.39, 17.52, 0.27 μM for MMP-3, MMP-8, MMP-9, MMP-13, respectively. Apigenin 7-O-β-D-glucuronide protects mice from LPS-induced endotoxin shock by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokine production, it may be used as a dietary complement for health promotion. |
| In vitro: |
| Planta Med . 2017 Jul;83(11):901-911. | | Correlating In Vitro Target-Oriented Screening and Docking: Inhibition of Matrix Metalloproteinases Activities by Flavonoids[Pubmed: 28288492] | | Abstract
Metalloproteases are a family of zinc-containing endopeptidases involved in a variety of pathological disorders. The use of flavonoid derivatives as potential metalloprotease inhibitors has recently increased.Particular plants growing in Sicily are an excellent yielder of the flavonoids luteolin, apigenin, and their respective glycoside derivatives (7-O-rutinoside, 7-O-glucoside, and 7-O-glucuronide).The inhibitory activity of luteolin, apigenin, and their respective glycoside derivatives on the metalloproteases MMP-1, MMP-3, MMP-13, MMP-8, and MMP-9 was assessed and rationalized correlating in vitro target-oriented screening and in silico docking.The flavones apigenin, luteolin, and their respective glucosides have good ability to interact with metalloproteases and can also be lead compounds for further development. Glycones are more active on MMP-1, -3, -8, and -13 than MMP-9. Collagenases MMP-1, MMP-8, and MMP-13 are inhibited by compounds having rutinoside glycones. Apigenin and luteolin are inactive on MMP-1, -3, and -8, which can be interpreted as a better selectivity for both -9 and -13 peptidases. The more active compounds are apigenin-7-O-rutinoside on MMP-1 and luteolin-7-O-rutinoside on MMP-3. The lowest IC50 values were also found for apigenin-7-O-glucuronide, apigenin-7-O-rutinoside, and luteolin-7-O-glucuronide. The glycoside moiety might allow for a better anchoring to the active site of MMP-1, -3, -8, -9, and -13. Overall, the in silico data are substantially in agreement with the in vitro ones (fluorimetric assay). | | Biomed Pharmacother . 2018 Nov;107:1505-1513. | | Scutellarin inhibits human renal cancer cell proliferation and migration via upregulation of PTEN[Pubmed: 30257368] | | Abstract
Background: Scutellarin is a naturally flavone glycoside that has been shown to exhibit anti-proliferative and anti-apoptotic activities among various human malignancies. However, the anti-cancer effect of Scutellarin in Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and the underlying mechanism remains unclear.
Methods and materials: RCC cell lines ACHN and 786-O were treated with different concentrations (0-210 μM) of Scutellarin in vitro. Cell viability and proliferation were investigated by MTT and colony formation assays. Cell invasion and migration were detected by Transwell assays. Cell apoptosis and cell cycle distribution was measured by flow cytometry. Western blot was used to investigate the expression levels of crucial proteins. Xenograft tumor model was established to evaluate tumor growth in vivo.
Results: Scutellarin significantly inhibited RCC cell proliferation in a dose- and time- dependent manner. Treatment of RCC cells with Scutellarin (30, 60, and 90 μM) markedly induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrested at G0/G1 phase in a concentration-dependent characteristic. Cell invasion and migration capacities of RCC cells were also dose-dependently suppressed by Scutellarin treatment. Western blot assays revealed that the crucial proteins including cyclin D1, CDK2, Bcl2, MMP-2, and MMP-9 were significantly reduced while Bax, cleaved caspase 3 and p21 were increased by Scutellarin in RCC cells. In vivo assay indicated that Scutellarin possessed anti-cancer effect on xenograft without triggering toxic effect. Mechanically, Scutellarin dramatically increased the protein level of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) and inhibited the activity of P13K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Ectopic expression of PTEN enhanced the inhibitory effect of Scutellarin on RCC proliferation while knockdown of PTEN abrogated it through regulating its downstream P13K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Conclusion: Scutellarin inhibited RCC cell proliferation and invasion partially by enhancing the expression of PTEN through inhibition of P13K/AKT/mTOR pathway, suggesting that Scutellarin might serve as a potential therapeutic agent in RCC treatment.
Keywords: P13K/AKT/mTOR; PTEN; Proliferation; Renal cancer; Scutellarin. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Food Funct. 2016 Feb;7(2):1002-13. | | Apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide inhibits LPS-induced inflammation through the inactivation of AP-1 and MAPK signaling pathways in RAW 264.7 macrophages and protects mice against endotoxin shock.[Pubmed: 26750400 ] | Apigenin-7-O-β-D-glucuronide (Apigenin-7-glucuronide,AG), an active flavonoid derivative isolated from the agricultural residue of Juglans sigillata fruit husks, possesses multiple pharmacological activities, including anti-oxidant, anti-complement, and aldose reductase inhibitory activities.
To date, no report has identified the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of AG.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study was therefore designed to characterize the molecular mechanisms of AG on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory cytokines in RAW 264.7 cells and on endotoxin-induced shock in mice. AG suppressed the release of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages in a dose-dependent manner without affecting cell viability. Additionally, AG suppressed LPS-induced mRNA expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and TNF-α. AG treatment decreased the translocation of c-Jun into the nucleus, and decreased activator protein-1 (AP-1)-mediated luciferase activity through the inhibition of both p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) phosphorylation. Consistent with the in vitro observations, AG protected mice from LPS-induced endotoxin shock by inhibiting proinflammatory cytokine production.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, these results suggest that AG may be used as a source of anti-inflammatory agents as well as a dietary complement for health promotion. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)