| In vitro: |
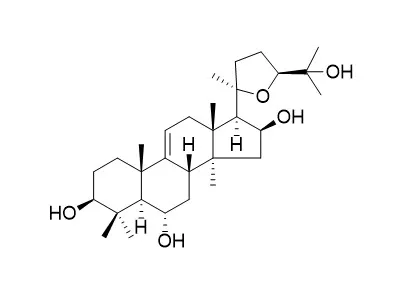
| Steroids . 2018 Jul;135:9-20. | | Cycloartane-type sapogenol derivatives inhibit NFκB activation as chemopreventive strategy for inflammation-induced prostate carcinogenesis[Pubmed: 29678446] | | Chronic inflammation is associated to 25% of cancer cases according to epidemiological data. Therefore, inhibition of inflammation-induced carcinogenesis can be an efficient therapeutic approach for cancer chemoprevention in drug development studies. It is also determined that anti-inflammatory drugs reduce cancer incidence. Cell culture-based in vitro screening methods are used as a fast and efficient method to investigate the biological activities of the biomolecules. In addition, saponins are molecules that are isolated from natural sources and are known to have potential for tumor inhibition. Studies on the preparation of analogues of cycloartane-type sapogenols (9,19-cyclolanostanes) have so far been limited. Therefore we have decided to direct our efforts toward the exploration of new anti-tumor agents prepared from cycloAstragenol and its production artifact Astragenol. The semi-synthetic derivatives were prepared mainly by oxidation, condensation, alkylation, acylation, and elimination reactions. After preliminary studies, five sapogenol analogues, two of which were new compounds (2 and 3), were selected and screened for their inhibitory activity on cell viability and NFκB signaling pathway activity in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. We found that the Astragenol derivatives 1 and 2 as well as cycloAstragenol derivatives 3, 4, and 5 exhibited strong inhibitory activity on NFκB signaling leading the repression of NFκB transcriptional activation and suppressed cell proliferation. The results suggested that these molecules might have significant potential for chemoprevention of prostate carcinogenesis induced by inflammatory NFκB signaling pathway. | | J Nat Prod . 2019 Nov 22;82(11):2979-2985. | | Microbial Transformation of Cycloastragenol and Astragenol by Endophytic Fungi Isolated from Astragalus Species[Pubmed: 31713424] | | Biotransformation of Astragalus sapogenins (cycloAstragenol (1) and Astragenol (2)) by Astragalus species originated endophytic fungi resulted in the production of five new metabolites (3, 7, 10, 12, 14) together with 10 known compounds. The structures of the new compounds were established by NMR spectroscopic and HRMS analysis. Oxygenation, oxidation, epoxidation, dehydrogenation, and ring cleavage reactions were observed on the cycloartane (9,19-cyclolanostane) nucleus. The ability of the compounds to increase telomerase activity in neonatal cells was also evaluated. After prescreening studies to define potent telomerase activators, four compounds were selected for subsequent bioassays. These were performed using very low doses ranging from 0.1 to 30 nM compared to the control cells treated with DMSO. The positive control cycloAstragenol and 8 were found to be the most active compounds, with 5.2- (2 nM) and 5.1- (0.5 nM) fold activations versus DMSO, respectively. At the lowest dose of 0.1 nM, compounds 4 and 13 provided 3.5- and 3.8-fold activations, respectively, while cycloAstragenol showed a limited activation (1.5-fold). |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)