| Cell Research: |
| Free Radic Biol Med. 2002 Apr 1;32(7):596-604. | | Flavonoids of Inula britannica protect cultured cortical cells from necrotic cell death induced by glutamate.[Pubmed: 11909694] | We previously reported 12 antioxidative flavonoids isolated from the n-BuOH extract of Inula britannica (Asteraceae). This prompted us to investigate further whether these flavonoids also showed antioxidative activity upon live cells grown in a culture system.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
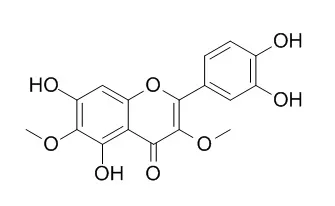
Among the 12 flavonoids tested, only patuletin, nepetin, and Axillarin protected primary cultures of rat cortical cells from oxidative stress induced by glutamate. These flavonoids exerted significant neuroprotective activity when they were administered either before or after the glutamate insult. Treatment with these flavonoids maintained the activities of such antioxidant enzymes as catalase, glutathione-peroxidase, and glutathione reductase, all of which play important roles in the antioxidative defense mechanism. Moreover, these three flavonoids also attenuated significant drops in glutathione induced by glutamate which is a routine concomitant of oxidative stress by inhibiting glutathione diminution. Accordingly, these flavonoids did not stimulate the synthesis of glutathione. With regard to structure-activity relationships, our results indicated that the 6-methoxyl group in the A ring and the 3', 4'-hydroxyl groups in the B ring are crucial for the protection against the oxidative stress; glycosylation greatly reduced their protective activities.
CONCLUSIONS:
Collectively, these results indicated that patuletin, nepetin, and Axillarin strongly protect primary cultured neurons against glutamate-induced oxidative stress. |
|
| Structure Identification: |
| J Nat Prod. 1999 Jul;62(7):1053-5. | | New guaianolides and xanthine oxidase inhibitory flavonols from ajania fruticulosa.[Pubmed: 10425142 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new guaianolides (1 and 2) were isolated from the aerial parts of Ajania fruticulosa along with a triterpene (alpha-amyrin), two plant sterols (beta-sitosterol and daucosterol), four flavonols [santin (3), Axillarin (4), centaureidin, and 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3, 3'-dimethoxyflavone], and five sesquiterpenes [ketoplenolide B, 9beta-hydroxyeudesma-4,11(13)-dien-12-oic acid, 9beta-acetoxyeudesma-4,11(13)-dien-12-oic acid, 1alpha,4alpha, 10alpha-trihydroxy-9alpha-angeloyloxyguaia-2,11(13)-dien-12, 6alpha-olide, and 3beta,4alpha-dihydroxyguaia-11(13),10(14)-dien-12, 6alpha-olide]. The structures of the new guaianolides were established as 1alpha-hydroperoxy-4beta,8alpha,10alpha, 13-tetrahydroxyguaia-2-en-12,6alpha-olide (1) and 1alpha-hydroperoxy-4alpha, 10alpha-dihydroxy-9alpha-angeloyloxyguaia-2,11(13)-dien-12, 6alpha-olide (2), respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Xanthine oxidase assays of all isolates revealed that santin (3) and
Axillarin (4) inhibited the enzyme with IC(50) values of 36.5 and 36.0 &mgr;M (that of allopurinol used as a positive control in the study was 24.2 &mgr;M), respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)