| In vitro: |
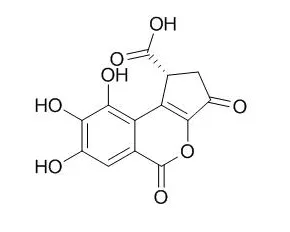
| African Journal of Biotechnology, 2007 , 6 (14) :1685-1689. | | In vitro assays for bioactivity-guided isolation of antisalmonella and antioxidant compounds in Thonningia sanginea flowers[Reference: WebLink] | Bioguided fractionation of the aqueous extract of Thonningia sanguinea flowers, used traditionally in the treatment of microbial diseases, led to the isolation of two phenolic compounds.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The structure of these compounds was elucidated by 1H, 13C 1D NMR and mass spectrometry experiments. The antibacterial activity against Salmonella strains and antioxidant activity of the crude extract, fractions and isolated compounds was evaluated using the DPPH method. The isolated compounds identified as Brevifolincarboxylic acid and gallic acid demonstrates moderate antibacterial activity against Salmonella enteritidis , Salmonella typhimurium , and Salmonella abony .
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicated that the two isolated compounds, gallic acid (IC50 = 13.5 μM) and Brevifolincarboxylic acid (IC50 = 18.0 μM) were mainly responsible for the good scavenging activity of the aqueous extract. | | Biol Pharm Bull. 2003 Dec;26(12):1754-60. | | Screening of the inhibitory effect of vegetable constituents on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated activity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin.[Pubmed: 14646185] | The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated nuclear transcription factor that mediates responses to environmental contaminants such as dioxins, which have many adverse health effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We performed a preliminary screening of the inhibitory effects of vegetable constituents on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD)-induced activation of AhR using the AhR-based bioassay for dioxins, the Ah-Immunoassay. Ninety vegetable constituents including flavonoids, tannins, saponins, terpenes, etc., were assayed in vitro. Among them, flavones, flavonols, anthraquinones, piperine, coumestrol, Brevifolincarboxylic acid, and resveratrol showed marked inhibitory effects on AhR-based bioassay activation by TCDD, and their effects were dose dependent. Curcumin, carnosol, and capsaicin also inhibited the activation of AhR in this assay, although to a lesser degree.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that several vegetable constituents might play a role in protection against dioxin toxicity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)