| J Nat Prod. 2012 Apr 27;75(4):591-8. |
| Bryonolic acid transcriptional control of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant genes in macrophages in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 22339499] |
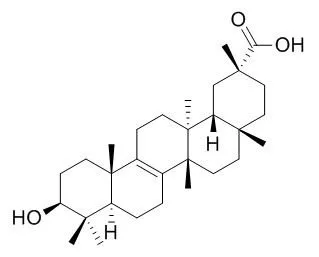
Bryonolic acid (BA) (1) is a naturally occurring triterpenoid with pleiotropic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
This study characterizes the mechanisms mediating the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities of BA and validates the utility of Bryonolic acid as a tool to explore the relationships between triterpenoid structure and activity. Bryonolic acid reduces the inflammatory mediator NO by suppressing the expression of the inflammatory enzyme inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in LPS-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. In addition, Bryonolic acid robustly induces the antioxidant protein heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) in vitro and in vivo in an Nrf2-dependent manner. Further analyses of Nrf2 target genes reveal selectivity for the timing and level of gene induction by Bryonolic acid in treated macrophages with distinct patterns for Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes. Additionally, the distinct expression profile of Bryonolic acid on Nrf2 target genes relative to oleanolic acid suggests the importance of the triterpenoid scaffold in dictating the pleiotropic effects exerted by these molecules. |
| J Nat Prod. 2010 Jun 25;73(6):1064-8. |
| Bryonolic acid: a large-scale isolation and evaluation of heme oxygenase 1 expression in activated macrophages.[Pubmed: 20481554] |
Bryonolic acid (BA) is a triterpenoid found in the Cucurbitaceae family of plants.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Our interests in the immunomodulatory effects of this class of natural products led us to discover that BA induces a marked increase in the expression of a phase 2 response enzyme, heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), in a dose-dependent manner. This phenotype has translational implications in malarial disease progression, and consequently we developed a large-scale isolation method for BA that will enable future in vitro and in vivo analyses.
CONCLUSIONS:
We have determined ideal growth conditions and time scale for maximizing BA content in the roots of Cucurbita pepo and analyzed BA production by HPLC. Large-scale extraction yielded 1.34% BA based on dry weight, allowing for the isolation of BA on a multigram scale. |
| Biol Pharm Bull. 1995 May;18(5):726-9. |
| Cytotoxic activity of bryonolic acid isolated from transformed hairy roots of Trichosanthes kirilowii var. japonica.[Pubmed: 7492990] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Bryonolic acid was isolated in high yield from transformed hairy root cultures of Trichosanthes kirilowii var. Japonica. Bryonolic acid exhibited cytotoxic activity to various tumor cells in vitro, independent of cell type. Normal cells such as rat hepatocytes are less sensitive to Bryonolic acid.
CONCLUSIONS:
The appearance of a DNA ladder was detected in the Bryonolic acid-treated HL-60RG cells, indicating that cell death triggered by Bryonolic acid is due to apoptosis. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)