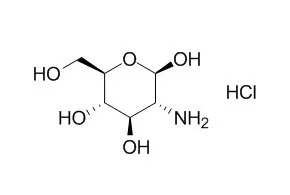
| Description: |
D-glucosamine hydrochloride has antimicrobial effect on the common 21 strains of food spoilage microorganisms, it could as preservative agent was used to preserve nature eleo juice. D-glucosamine hydrochloride also has antitumor, antiinflammaty, and anti-arthritis effects, it induces cell apoptosis by blocking of cell-cycle. |
| Targets: |
TGF-β/Smad | TNF-α | COX | NOS | IL Receptor | Calcium Channel |
| In vitro: |
| Chinese Journal of Marine Drugs, 2008, 27(6):20-5. | | Effects of D-glucosamine hydrochloride on the cell-cycle and expression of proteins in gastric carcinoma cell SGC-7901[Reference: WebLink] | To study the effects of D-Glucosamine hydrochloride on the apoptosis of gastric carcinoma cell line SGC-7901 and its mechanism.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
SRB assay was used to examine the effects of D-Glucosamine hydrochloride on the growth inhibition of SGC-7901.The cell-cycle and expression of cytochrome-C were observed by flow cytometry,the concentrations of intracellular Ca2+ was determined by CLSM and the expressions of cyclinB1,calcinerin were investigated by Western-Blot. D-Glucosamine hydrochloride could block SGC-7901 cell-cycle at S phase of cell division,increase the concentration of intracellular Ca2+ and decrease the expression of cyclinB1,the expressions of calcinerin and cytochrome-c were increased respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
Block of cell-cycle may be one of the mechanism of inducing cell apoptosis by D-Glucosamine hydrochloride. | | Fisheries Science, 2001, 18(2):14-5. | | Studies on Antimicrobial Effects of D-glucosamine Hydrochloride.[Reference: WebLink] | The antimicrobial effect of D-Glucosamine hydrochloride(GAH)was investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
It was found that GAH had antimicrobial effects on the common 21 strains of food spoilage microorganisms.The minimal inhibition concentration is 0 5 g/L,for mould is 2 g/L,for yeast is 1 g/L.In addition,it showed better preservation effect while GAH as preservative agent was used to preserve nature eleo juice. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Mar Drugs. 2012 Aug;10(8):1873-82. | | Metabolomic analyses of blood plasma after oral administration of D-glucosamine hydrochloride to dogs.[Pubmed: 23015778 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
D-Glucosamine hydrochloride (GlcN∙HCl) is an endogenous amino monosaccharide synthesized from glucose that is useful in the treatment of joint diseases in both humans and animals. The aim of this study was to examine amino acid metabolism in dogs after oral administration of GlcN∙HCl. Accelerated fumarate respiration and elevated plasma levels of lactic acid and alanine were observed after administration.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that oral administration of GlcN∙HCl induces anaerobic respiration and starvation in cells, and we hypothesize that these conditions promote cartilage regeneration. Further studies are required to evaluate the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β). | | Phytother Res. 2014 Jul;28(7):1054-63 | | Effect of fucoxanthin alone and in combination with D-glucosamine hydrochloride on carrageenan/kaolin-induced experimental arthritis in rats.[Pubmed: 24338843] | The objective of the present study was to investigate the effect of the fucoxanthin (FUCO) alone and in combination with glucosamine hydrochloride (GAH) on carrageenan/kaolin-induced inflammatory arthritis model in rats and to explore its underlying mechanisms.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Joint swelling, muscle weight ratio (%), histopathological examination and scoring, and proteoglycan degradation were examined. Pro-inflammatory interleukin (IL-1β) and tumor necrosis (TNF-α) levels, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and inducible nitric oxide synthase(iNOS) protein expression and nitric oxide (NO) level in knee synovial tissue extract were analyzed using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, western blotting analysis, and Griess reagent assay, respectively. FUCO and FUCO + GAH not only may significantly reduce degrees of knee joint swelling and prevent against muscle atrophy, but also may significantly attenuate inflammation in synovial tissue, cartilage erosion, and proteoglycan loss. The efficacies of FUCO + GAH were stronger than that of GAH or FUCO. FUCO alone and FUCO + GAH can significantly inhibit upregulation of COX-2 and iNOS protein expressions, decrease of IL-1β and TNF-α levels, and reduce NO production in knee synovial tissue extract.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicated that FUCO is an effective anti-arthritis agent through an antiinflammation mechanism. FUCO may enhance therapeutic effect of GAH on rat arthritis through mechanism of antiinflammation. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)