| In vitro: |
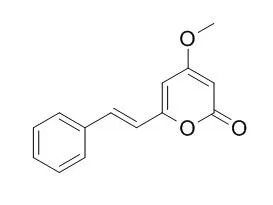
| PLoS One. 2013 Oct 15;8(10):e77626. | | A plant kavalactone desmethoxy yangonin prevents inflammation and fulminant hepatitis in mice.[Pubmed: 24143247] | An active compound of the plant rhizomes, Desmethoxy yangonin (DMY), was identified in this study for its novel effect against endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated inflammation in murine macrophages and LPS/D-galactosamine (LPS/D-GalN)-induced fulminant hepatitis in mice.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Desmethoxy yangonin was observed to significantly inhibit proliferation and activation of T cells ex vivo and the activity of several pro-inflammatory mediators in vitro. Desmethoxy yangonin also protected LPS/D-GalN-induced acute hepatic damages in mice through inhibiting aminotransferases activities and infiltrations of inflammatory macrophages, neutrophils and pathogenic T cells into the liver tissues. In addition, pretreatment with Desmethoxy yangonin significantly improved the survival rate of LPS/D-GalN-treated mice to 90% (9/10), compared to LPS/D-GalN-treated group (40%, 4/10). UPLC/MS platform-based comparative metabolomics approach was used to explore the serum metabolic profile in fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) mice with or without the Desmethoxy yangonin pretreatment. The results showed that LPS/D-GalN-induced hepatic damage is likely through perturbing amino acid metabolism, which leads to decreased pyruvate formation via catalysis of aminotransferases, and Desmethoxy yangonin treatment can prevent to a certain degree of these alterations in metabolic network in mouse caused by LPS/D-GalN.
CONCLUSIONS:
Mechanistic investigation demonstrated that Desmethoxy yangonin protects LPS or LPS/D-GalN-induced damages in cell or liver tissues mainly through de-regulating IKK/NFκB and Jak2/STAT3 signaling pathways. | | Planta Med., 2015, 81 - PB19 | | Isolation and characterization of desmethoxyyangonin from Renealmia alpinia as a selective reversible inhibitor of human Monoamine Oxidase B.[Reference: WebLink] | Renealmia alpinia (Zingiberaceae), a medicinal plant of tropical rainforests, is used to treat snakebites, as a febrifuge, analgesic, antiemetic, antiulcer, and anticonvulsant. The dichloromethane extract of R. alpinia leaves showed potent inhibition of recombinant human MAO-A and -B.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Phytochemical studies yielded six known compounds including, pinostrobin, pinostrobin chalcone, sakuretin, sakuretin-4'-methyl, yashabushidiol, and Desmethoxy yangonin. Desmethoxy yangonin displayed strong inhibition of MAO-A and -B (Ki values 0.922 and 0.031μM, respectively), with about 30 fold more selectivity against MAO-B. The kinetic analysis of the inhibition and equilibrium dialysis dissociation assay of the enzyme-inhibitor complex showed reversible binding of
CONCLUSIONS:
Desmethoxy yangonin with MAO-A and -B. Selective reversible inhibitors of MAO-B have important therapeutic value for treatment of neurodegenerative disorders and Parkinson's Disease. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)