| In vitro: |
| Planta Med. 2013 Jul;79(11):933-8. | | Dodoviscin a inhibits melanogenesis in mouse b16-f10 melanoma cells.[Pubmed: 23804039] | Nowadays, abnormal hyperpigmentation in human skin such as melasma, freckles, and chloasma has become a serious esthetic problem. Cutaneous depigmenting agents could be used to treat these hyperpigmentation-associated dieseases. Dodoviscin A is a natural product isolated from the aerial parts of Dodonaea viscosa.
In the present study, we evaluated the effect of Dodoviscin A on melanin production in B16-F10 melanoma cells for the first time.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We found that Dodoviscin A inhibited melanin biosynthesis induced by 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and PD98059 significantly, and there was no obvious effect on the viability of Dodoviscin A-treated B16-F10 cells. Meanwhile, Dodoviscin A could suppress the activity of mushroom tyrosinase in the cell-free assay system and also decrease 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine-induced tyrosinase activity and expression of mature tyrosinase protein in B16-F10 cells. Western blotting analysis showed that Dodoviscin A inhibited 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine and forskolin-induced phosphorylation of the cAMP response element binding protein in B16-F10 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results indicate that Dodoviscin A may be a new promising pigmentation-altering agent for cosmetic and therapeutic applications. | | J Nat Prod. 2012 Apr 27;75(4):699-706. | | Isoprenylated flavonoid and adipogenesis-promoting constituents of Dodonaea viscosa.[Pubmed: 22512738] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
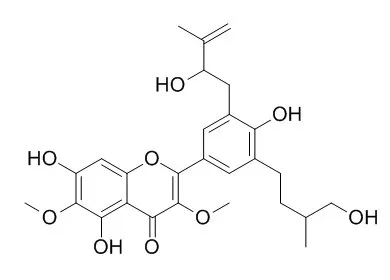
Ten new isoprenylated flavonol derivatives, Dodoviscin A, dodoviscins B
-J (1-10), and seven known compounds (11-17) were isolated from the aerial parts of Dodonaea viscosa. Compounds 1, 2, 4, 5, 7-9, 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3',5'-bis(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-3-methoxyflavone (11), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3',5'-bis(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-3,6-dimethoxyflavone (12), 5,7,4'-trihydroxy-3'-(4-hydroxy-3-methylbutyl)-5'-(3-methyl-2-buten-1-yl)-3,6-dimethyoxyflavone (13), sakuranetin (14), and blumeatin (15) promoted adipocyte differentiation as characterized by increased triglyceride levels in 3T3L1 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 1, 13, and 15 also enhanced the accumulation of lipid droplets and induced upregulation of the expression of the adipocyte-specific genes aP2 and GLUT4. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)