| Description: |
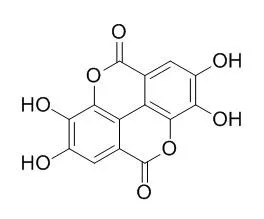
Ellagic acid is a potent and ATP-competitive CK2 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 40 nM and a Ki of 20 nM. Ellagic acid has anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative and antioxidant properties, it can prevent cognitive and LTP deficits and also prevent brain inflammation following TBI. Ellagic acid reduced the expression of NO, MDA, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-2 and NF-κB, and induced the production of GSH and IL-10. |
| In vitro: |
| Environ Toxicol. 2014 Nov;29(11):1262-74. | | Ellagic acid induces apoptosis in TSGH8301 human bladder cancer cells through the endoplasmic reticulum stress- and mitochondria-dependent signaling pathways.[Pubmed: 23554011] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To investigate the effects of Ellagic acid on the growth inhibition of TSGH8301 human bladder cancer cells in vitro, cells were incubated with various doses of Ellagic acid for different time periods. The phase-contrast microscope was used for examining and photographing the morphological changes in TSGH8301 cells. Flow cytometric assay was used to measure the percentage of viable cells, cell cycle distribution, apoptotic cells, ROS, mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), Ca(2+) , caspase-9 and -3 activities in TSGH8301 cells after exposure to Ellagic acid. Western blotting was used to examine the changes of cell cycle and apoptosis associated proteins levels. Results indicated that Ellagic acid induced morphological changes, decreased the percentage of viable cells through the induction of G0/G1 phase arrest and apoptosis, and also showed that Ellagic acid promoted ROS and Ca(2+) productions and decreased the level of ΔΨm and promoted activities of caspase-9 and -3. The induction of apoptosis also confirmed by annexin V staining, comet assay, DAPI staining and DNA gel electrophoresis showed that Ellagic acid induced apoptosis and DNA damage in TSGH8301 cells. Western blotting assay showed that Ellagic acid promoted p21, p53 and decreased CDC2 and WEE1 for leading to G0/G1 phase arrest and promoting BAD expression, AIF and Endo G, cytochrome c, caspase-9 and -3 for leading to apoptosis in TSGH8301 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
On the basis of these observations, we suggest that Ellagic acid induced cytotoxic effects for causing a decrease in the percentage of viable cells via G0/G1 phase arrest and induction of apoptosis in TSGH8301 cells. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). 2014 Oct;98(5):936-41. | | Effect of ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss).[Pubmed: 24401136] | In this study, effect of Ellagic acid on some haematological, immunological and antioxidant parameters in the blood and various tissues of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) were examined.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Four groups of rainbow trout were fed experimental diets containing either no Ellagic acid (control) or supplemented with Ellagic acid at 50 mg/kg diet (EA-50), 100 mg/kg diet (EA-100) or 150 mg/kg diet (EA-150) for 21 days. Samples of the blood and tissue (liver, kidney and spleen) were collected at the end of the experiment and analysed for their haematological profile (the red blood cell count, the haemoglobin concentration and the haematocrit level), immune response (the white blood cell count, the oxidative radical production (NBT activity), the total plasma protein and total immunoglobulin level) and oxidant/antioxidant status (the malondialdehyde level, the superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase activity as well as the reduced glutathione concentration).
CONCLUSIONS:
The findings of this study demonstrated that Ellagic acid had a positive effect on the haematological parameters, the immune response and the antioxidant enzyme activities of the fish. | | Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):290-9. | | Ellagic acid protects against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation through inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B, inducible cyclooxygenase and proinflammatory cytokines and enhancement of interleukin-10 via an antioxidant mechanism.[Pubmed: 24534771] | There are several hypotheses that explain the process of acute inflammation, including free radical overproduction, pro-inflammatory enzyme activation, and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this study, the protective role of Ellagic acid against carrageenan-induced acute inflammation was assessed. In addition, the immunomodulatory action, the antioxidant effects, and the role of COX-2 and NF-κB were also investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Inflammation was induced by the injection of 100 μl of 1.5% carrageenan solution. Ellagic acid (10, 25, 50, 100 and 200mg/kg), indomethacin (10 mg/kg), meloxicam (4 mg/kg), and saline, were injected 2h before carrageenan injection. The percentage inhibition in the paw weight was calculated. Paws, MDA, NO, GSH, IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-10 and NF-κB mRNA expression were estimated. Formalin fixed hind paws were used for histopathological examination and immunohistochemical staining for COX-2 expression. Ellagic acid, meloxicam and indomethacin reduced paws, edema, MDA and NO formation. In addition, all of them restored the depleted GSH contents in the paws. Ellagic acid, meloxicam and indomethacin reduced NF-κB mRNA expression. Ellagic acid ameliorated COX-2 expression; meloxicam inhibited while indomethacin failed. Both Ellagic acid and meloxicam increased IL-10 while indomethacin did not.
CONCLUSIONS:
The docking study revealed a high affinity of Ellagic acid towards COX-2. Ellagic acid exhibited a potent anti-inflammatory effect against carrageenan-induced inflammation. The mechanisms of Ellagic acid induced protection were proved to be due to reduction of NO, MDA, IL-1β, TNF-α, COX-2 and NF-κB expression and induction of GSH and IL-10 production. | | J Biochem Mol Toxicol . 2017 Dec;31(12). | | Prophylactic effects of ellagic acid and rosmarinic acid on doxorubicin-induced neurotoxicity in rats[Pubmed: 28815802] | | Abstract
Doxorubicin (DOX) is a chemotherapeutic agent widely used in human malignancies. Its long-term use cause neurobiological side effects. The aim of the present study was to investigate the prophylactic effect exerted by daily administration of Ellagic acid (EA) and rosmarinic acid (RA) on DOX-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Our data showed that DOX-induced significant elevation of brain malondialdehyde, tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), caspase-3, and cholinesterase associated with significant reduction in reduced glutathione, monoamines namely serotonin, dopamine, as well as norepinephrine. Concomitant administration of EA (10 mg/kg/day, p.o. for 14 days) and/or RA (75 mg/kg/day, p.o. for 14 days) with DOX significantly mitigated the neural changes induced by DOX. Meanwhile, treatment ameliorated pro-inflammatory cytokines as TNF-α, iNOS, and attenuated oxidative stress biomarkers as well as brain monoamines. In conclusion, EA and RA can effectively protect against DOX-induced neurotoxicity, and the mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective effect are potentially associated with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic properties.
Keywords: brain; doxorubicin; Ellagic acid; rats; rosmarinic acid. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)