| In vitro: |
| Mol Med Rep. 2017 Aug;16(2):1298-1306. | | Eriodictyol 7‑O‑β‑D glucopyranoside from Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt. ameliorates lipid disorders via protecting mitochondrial function and suppressing lipogenesis.[Pubmed: 28627652] |
Coreopsis tinctoria (snow chrysanthemum) has been reported to exert antihyperlipidemic effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The present study aimed to identify the active compounds of Coreopsis tinctoria and to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying its effects on lipid dysregulation by measuring lipid levels, reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation and fatty acid synthesis.
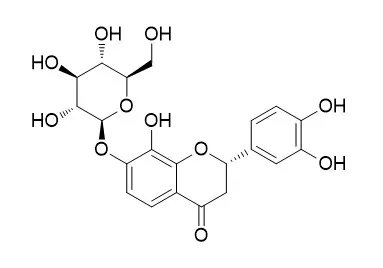
The present results demonstrated that snow chrysanthemum aqueous extracts significantly reduced serum lipid levels and oxidative stress in vivo. The main compounds that were isolated were identified as Flavanomarein (compound 1) and eriodictyol 7‑O‑β‑D glucopyranoside (compound 2). Compounds 1 and 2 demonstrated potent antioxidative properties, including free radical scavenging activity, inhibition of lipid peroxidation, as well as lipid‑lowering effects in human HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells treated with free fatty acids (FFAs). Compound 2 was revealed to suppress the elevation of triglyceride levels and inhibit lipid peroxidation following FFA treatment. In addition, it was demonstrated to significantly reduce intracellular levels of reactive oxygen species and improve the mitochondrial membrane potential and adenosine triphosphate levels, thus protecting mitochondrial function in FFA‑treated HepG2 cells. Furthermore, compound 2 markedly suppressed the protein expression levels of disulfide‑isomerase A3 precursor and fatty acid synthase, thus suppressing FFA‑induced lipogenesis in HepG2 cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, the present study identified compound 2 as one of the main active compounds in Coreopsis tinctoria responsible for its lipid‑lowering effects. Compound 2 was revealed to possess antihyperlipidemic properties, exerted via reducing oxidative stress, protecting mitochondrial function and suppressing lipogenesis. | | Acta Pol Pharm. 2007 Sep-Oct;64(5):441-7. | | Antioxidant activity of extracts and flavonoids from Bidens tripartita.[Pubmed: 18540165] | Extracts from herb and flowers of Bidens tripartita L. (Asteraceae), obtained using solvents of different polarity, were studied for their radical scavenging effects.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antioxidant activities of pure flavonoids: Flavanomarein (isookanin 7-O-glucoside), cynaroside (luteolin 7-O-glucoside) and luteolin, which had been isolated from this plant, were also evaluated. Radical-scavenging activity was measured by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy using stable 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) radical. The content of flavonoids in flower heads is half of that found in the herb; however, the extract from flowers showed that the antioxidant activity was almost two times higher there. Some extracts (n-BuOH fraction) showed long lasting radical scavenging activity and the EPR spectra were recorded in time to follow the reaction kinetics.
CONCLUSIONS:
Scavenging of DPPH showed second-order kinetics at the beginning of the assay period and later the first-order one. Different kinetics suggested the presence of polymerized and/or less active antioxidants with different scavenging mechanisms for particular polyphenolic compounds. Bur-marigold extracts are a potential source of natural antioxidants that may be used in pharmaceutical or food industry. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)