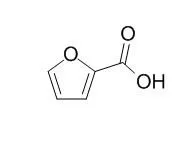
| In vitro: |
| PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41142. | | Trace amounts of furan-2-carboxylic acids determine the quality of solid agar plates for bacterial culture.[Pubmed: 22848437] | Many investigators have recognised that a significant proportion of environmental bacteria exist in a viable but non-culturable state on agar plates, and some researchers have also noticed that some of such bacteria clearly recover their growth on matrices other than agar. However, the reason why agar is unsuitable for the growth of some bacteria has not been addressed.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
According to the guide of a bioassay for swarming inhibition,We identified 5-hydroxymethylFuran-2-carboxylic acid (5-HMFA) and Furan-2-carboxylic acid (FA) as factors that inhibit bacterial swarming and likely inhibit extracellular polysaccharide production on agar. The Furan-2-carboxylic acids 5-HMFA and Furan-2-carboxylic acid effectively inhibited the swarming and swimming of several environmental bacteria at concentrations of 1.8 and 2.3 µg L(-1) (13 and 21 nmol L(-1)), respectively, which are equivalent to the concentrations of these compounds in 0.3% agar. On Luria-Bertani (LB) plates containing 1.0% agar that had been previously washed with MeOH, a mixture of 5-HMFA and Furan-2-carboxylic acid in amounts equivalent to their original concentrations in the unwashed agar repressed the swarming of Escherichia coli K12 strain W3110, a representative swarming bacterium.
CONCLUSIONS:
Agar that contains trace amounts of 5-HMFA and Furan-2-carboxylic acid inhibits the proliferation of some slow-growing or difficult-to-culture bacteria on the plates, but it is useful for single colony isolation due to the ease of identification of swarmable bacteria as the non-swarmed colonies. |
|
| In vivo: |
| J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006 Aug;318(2):555-62. | | An orally active cathepsin K inhibitor, furan-2-carboxylic acid, 1-{1-[4-fluoro-2-(2-oxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-phenyl]-3-oxo-piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl}-cyclohexyl)-amide (OST-4077), inhibits osteoclast activity in vitro and bone loss in ovariectomized rats.[Pubmed: 16699068] | Human cathepsin K, a cysteine proteinase of the papain family, has been recognized as a potential drug target for the treatment of osteoporosis. The predominant expression of cathepsin K in osteoclasts has rendered the enzyme into a major target for the development of novel antiresorptive drugs.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Now, we report the pharmacological properties of OST-4077 [Furan-2-carboxylic acid (1-{1-[4-fluoro-2-(2-oxo-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-phenyl]-3-oxo-piperidin-4-ylcarbamoyl}-cyclohexyl)-amide] as a novel selective cathepsin K inhibitor. Human and rat cathepsin K were inhibited in vitro by Furan-2-carboxylic acid with the IC50 values of 11 and 427 nM, respectively. Furan-2-carboxylic acid suppressed bone resorption induced by rabbit osteoclasts (IC50, 37 nM) but did not affect bone mineralization or cellular alkaline phosphatase activity in MC3T3-E1 cells. Parathyroid hormone-induced bone resorption was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner in thyroparathyroidectomized rats gavaged with a single dose of Furan-2-carboxylic acid (ED50, 69 mg/kg). When given orally twice daily for 4 weeks to 3-month-old ovariectomized (OVX) rats, Furan-2-carboxylic acid dose-dependently prevented bone loss, as monitored by bone densitometry, ash content, and urinary excretion of deoxypyridinoline. No change in serum osteocalcin in the OVX rats by Furan-2-carboxylic acid suggested that bone formation might not be affected by the agent.
CONCLUSIONS:
In summary, Furan-2-carboxylic acid selectively inhibited bone resorbing activities of osteoclasts and prevented bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency but did not affect bone formation. Furan-2-carboxylic acid, an orally active selective human cathepsin K inhibitor, may have the therapeutic potential for the treatment of diseases characterized by excessive bone loss including osteoporosis. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)