| In vitro: |
| Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2005 Jan;53(1):121-4. | | Neolignans from Piper futokadsura and their inhibition of nitric oxide production.[Pubmed: 15635246] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
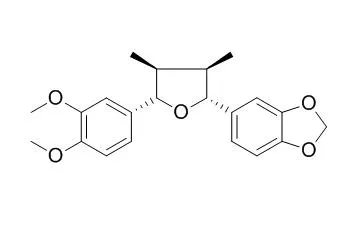
From a MeOH extract of the aerial part of Piper futokadsura, the tetrahydrofuran lignans, futokadsurin A [(7S,8S,7'S,8'R)-3,4,3'-trimethoxy-4'-hydroxy-7,7'-epoxylignan], futokadsurin B [(7R,8R,7'R,8'S)-3,4-dimethoxy-3',4'-methylenedioxy-7,7'-epoxylignan], and Futokadsurin C [(7R,8R,7'S,8'S)-3,4-methylenedioxy-3',4'-dimethoxy-7,7'-epoxylignan] were isolated, together with nine known neolignans. In addition, L-tryptophan, pellitorine, phytol, elemicin, and 1,2,4-trimethoxyphenyl-5-aldehyde were isolated. The structures of the new compounds were elucidated using spectroscopic methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
These lignans inhibited nitric oxide production by a murine macrophage-like cell line (RAW 264.7), which was activated by lipopolysaccharide and interferon-gamma. | | Phytochemistry Letters, 2015, 13:200-205. | | Aryltetralols from Holostylis reniformis and syntheses of lignan analogous.[Reference: WebLink] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Two new lignans, an aryltetralol and its methyl ether analogous, were isolated from Holostylis reniformis (Aristolochiaceae) together with Futokadsurin C and (−)-8′-epi-aristoligone. The latter was also obtained as an enantiomeric mixture by synthesis and was transformed into aryltetralols and aryltetralenes that were subjected to chiral-HPLC separations. The compound structures were determined by spectroscopic methods.
CONCLUSIONS:
Several of these lignans had their antiplasmodial activity (against Plasmodium falciparum, W2 clone, anti-HRPII) and toxicity to mammalian kidney cells (MDL50) evaluated. (−)-Cyclogalgravin and (−)-aristoligol exhibited activity (IC50 ~ 10.8 and 8.4 μM, respectively), the latter exhibited lower toxicity. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)