| Kinase Assay: |
| Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2010;74(4):878-80. | | Inhibitory activity against urease of quercetin glycosides isolated from Allium cepa and Psidium guajava.[Pubmed: 20378972] | Methanolic extracts of edible plants and seaweeds were tested for their inhibitory activity against Jack bean urease.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Quercetin-4'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside was isolated from Allium cepa as a urease inhibitor with an IC(50) value of 190 microM-. Quercetin and two quercetin glycosides, avicularin and Guaijaverin, were isolated from Psidium guajava as urease inhibitors with respective IC(50) values of 80 microM-, 140 microM-, and 120 microM-. | | Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo). 2002, 50(6): 788-95. | | The methanolic extracts of several natural medicines and medicinal foodstuffs were found to show an inhibitory effect on rat lens aldose reductase. In most cases, flavonoids were isolated as the active constituents by bioassay-guided separation, and among[Pubmed: 12045333] | The methanolic extracts of several natural medicines and medicinal foodstuffs were found to show an inhibitory effect on rat lens aldose reductase.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In most cases, flavonoids were isolated as the active constituents by bioassay-guided separation, and among them, quercitrin (IC(50)=0.15 microM), Guaijaverin (0.18 microM), and desmanthin-1 (0.082 microM) exhibited potent inhibitory activity. Desmanthin-1 showed the most potent activity, which was equivalent to that of a commercial synthetic aldose reductase inhibitor, epalrestat (0.072 microM). In order to clarify the structural requirements of flavonoids for aldose reductase inhibitory activity, various flavonoids and related compounds were examined.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results suggested the following structural requirements of flavonoid: 1) the flavones and flavonols having the 7-hydroxyl and/or catechol moiety at the B ring (the 3',4'-dihydroxyl moiety) exhibit the strong activity; 2) the 5-hydroxyl moiety does not affect the activity; 3) the 3-hydroxyl and 7-O-glucosyl moieties reduce the activity; 4) the 2-3 double bond enhances the activity; 5) the flavones and flavonols having the catechol moiety at the B ring exhibit stronger activity than those having the pyrogallol moiety (the 3',4',5'-trihydroxyl moiety). |
|
| Structure Identification: |
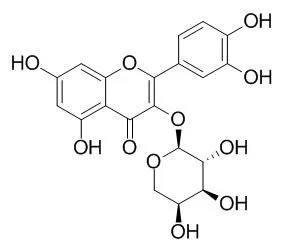
| Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2012 Nov;97:449-55. | | Exploring the binding mechanism of Guaijaverin to human serum albumin: fluorescence spectroscopy and computational approach.[Pubmed: 22820048] | The Guaijaverin (Gua) is a polyphenolic substance which exhibits some pharmacological activities such as antibacterial and antioxidant activities.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here we have investigated the binding of Gua with human serum albumin (HSA) at physiological pH 7.0. In this study, the fluorescence spectroscopy, ab initio and molecular modeling calculations were applied. The Stern-Volmer quenching constant (K(SV)) and its modified form (K(a)) were calculated at 298, 303 and 308 K, with the corresponding thermodynamic parameters ΔH, ΔG and ΔS as well. The fluorescence quenching method was used to determine the number of binding sites (n) and binding constants (K(b)) values at 298, 303 and 308 K. The distance between donor (HSA) and acceptor (Gua) was estimated according to fluorescence resonance energy transfer. The geometry optimization of Gua was performed in its ground state by using ab initio DFT/B3LYP functional with a 6-31G(d,p) basis set used in calculations.
CONCLUSIONS:
Molecular modeling calculation indicated that the Gua is located within the hydrophobic pocket of the subdomain IIA of HSA. The theoretical results obtained by molecular modeling were corroborated by fluorescence spectroscopy data. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)