| Structure Identification: |
| Metab Eng. 2015 Sep;31:84-93. | | Assembly of a novel biosynthetic pathway for production of the plant flavonoid fisetin in Escherichia coli.[Pubmed: 26192693 ] | Plant secondary metabolites are an underutilized pool of bioactive molecules for applications in the food, pharma and nutritional industries. One such molecule is fisetin, which is present in many fruits and vegetables and has several potential health benefits, including anti-cancer, anti-viral and anti-aging activity. Moreover, fisetin has recently been shown to prevent Alzheimer's disease in mice and to prevent complications associated with diabetes type I. Thus far the biosynthetic pathway of fisetin in plants remains elusive.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we present the heterologous assembly of a novel fisetin pathway in Escherichia coli. We propose a novel biosynthetic pathway from the amino acid, tyrosine, utilizing nine heterologous enzymes. The pathway proceeds via the synthesis of two flavanones never produced in microorganisms before--Garbanzol and resokaempferol.
CONCLUSIONS:
We show for the first time a functional biosynthetic pathway and establish E. coli as a microbial platform strain for the production of fisetin and related flavonols. | | Nat Prod Res. 2015;29(12):1177-9. | | Radical scavenging activities of flavonoids from roots of Akschindlium godefroyanum.[Pubmed: 25426867 ] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
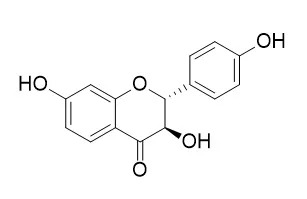
Chemical constituents of crude ethyl acetate extract of roots of Akschindlium godefroyanum (Kuntze) H. Ohashi were investigated and seven flavonoids were isolated. Their structures were identified based on spectroscopic methods as well as by comparison with spectral data reported in the literature as six flavanonols and a flavonol including 7,4'-dihydroxy-5,3'-dimethoxyflavanonol (1), neophellamuretin (2), taxifolin (3), erycibenin D (4), geraldol (5), fustin (6) and Garbanzol (7). Compounds 2, 4 and 7 were found in the genus Akschindlium for the first time.
CONCLUSIONS:
Compounds 3, 5 and 6 appeared to have free radical scavenging activities using DPPH assay with IC50 of 21, 40 and 15 μg/mL, respectively. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)