| Description: |
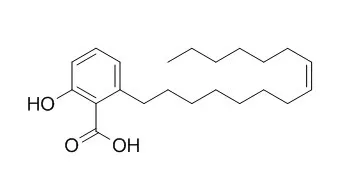
Ginkgolic acid C15:1 has antibacterial, antiparasitic, and anti-cancer activities, it can suppress lung cancer invasion and migration through the inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.
|
| Targets: |
PI3K | Akt | mTOR | TGF-β/Smad | Antifection |
| In vitro: |
| Int J Food Microbiol. 2014 Mar 17;174:47-55. | | Ginkgolic acids and Ginkgo biloba extract inhibit Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation.[Pubmed: 24457153] | Infection by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7 (EHEC) is a worldwide problem, and there is no effective therapy. Biofilm formation is closely related to EHEC infection and is also a mechanism of antimicrobial resistance.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antibiofilm screening of 560 purified phytochemicals against EHEC showed that Ginkgolic acid C15:1 and ginkgolic acid C17:1 at 5μg/ml and Ginkgo biloba extract at 100μg/ml significantly inhibited EHEC biofilm formation on the surfaces of polystyrene and glass, and on nylon membranes. Importantly, at their working concentrations, ginkgolic acids and G. biloba extract did not affect bacterial growth. Transcriptional analyses showed that Ginkgolic acid C15:1 repressed curli genes and prophage genes in EHEC, and these findings were in-line with reduced fimbriae production and biofilm reductions. Interestingly, ginkgolic acids and G. biloba extract did not inhibit the biofilm formation of a commensal E. coli K-12 strain. In addition, ginkgolic acids and G. biloba extract inhibited the biofilm formation of three Staphylococcus aureus strains.
CONCLUSIONS:
The findings of this study suggest that plant secondary metabolites represent an important resource for biofilm inhibitors. | | BMC Biotechnol. 2017; 17: 5. | | The antibacterial activity and mechanism of ginkgolic acid C15:1.[Pubmed: 28088196] | The present study investigated the antibacterial activity and underlying mechanisms of Ginkgolic acid C15:1(GA (C15:1)) monomer using green fluorescent protein (GFP)-labeled bacteria strains.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
GA presented significant antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria but generally did not affect the growth of Gram-negative bacteria. The studies of the antibacterial mechanism indicated that large amounts of GA (C15:1) could penetrate GFP-labeled Bacillus amyloliquefaciens in a short period of time, and as a result, led to the quenching of GFP in bacteria. In vitro results demonstrated that GA (C15:1) could inhibit the activity of multiple proteins including DNA polymerase. In vivo results showed that GA (C15:1) could significantly inhibit the biosynthesis of DNA, RNA and B. amyloliquefaciens proteins.
CONCLUSIONS:
We speculated that GA (C15:1) achieved its antibacterial effect through inhibiting the protein activity of B. amyloliquefaciens. GA (C15:1) could not penetrate Gram-negative bacteria in large amounts, and the lipid soluble components in the bacterial cell wall could intercept GA (C15:1), which was one of the primary reasons that GA (C15:1) did not have a significant antibacterial effect on Gram-negative bacteria. | | Toxicol Appl Pharmacol . 2018 Apr 15;345:1-9. | | Pharmacological inhibition of SUMO-1 with ginkgolic acid alleviates cardiac fibrosis induced by myocardial infarction in mice[Pubmed: 29524504] | | Abstract
Background and purpose: Protein modification by small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of heart diseases. The present study was designed to determine whether ginkgolic acid (GA) as a SUMO-1 inhibitor exerts an inhibitory effect on cardiac fibrosis induced by myocardial infarction (MI).
Experimental approach: GA was delivered by osmotic pumps in MI mice. Masson staining, electron microscopy (EM) and echocardiography were used to assess cardiac fibrosis, ultrastructure and function. Expression of SUMO-1, PML, TGF-β1 and Pin1 was measured with Western blot or Real-time PCR. Collagen content, cell viability and myofibroblast transformation were measured in neonatal mouse cardiac fibroblasts (NMCFs). Promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein was over-expressed by plasmid transfection.
Key results: GA improved cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction, and decreased SUMO-1 expression in MI mice. GA (>20 μM) inhibited NMCF viability in a dose-dependent manner. Nontoxic GA (10 μM) restrained angiotensin II (Ang II)-induced myofibroblast transformation and collagen production. GA also inhibited expression of TGF-β1 mRNA and protein in vitro and in vivo. GA suppressed PML SUMOylation and PML nuclear body (PML-NB) organization, and disrupted expression and recruitment of Pin1 (a positive regulator of TGF-β1 mRNA), whereas over-expression of PML reversed that.
Conclusions and implications: Inhibition of SUMO-1 by GA alleviated MI-induced heart dysfunction and fibrosis, and the SUMOylated PML/Pin1/TGF-β1 pathway is crucial for GA-inhibited cardiac fibrosis. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Aquaculture, 2009, 297(1-4):38-43. | | In vivo assessment of anthelmintic efficacy of ginkgolic acids (C13:0, C15:1) on removal of Pseudodactylogyrus in European eel.[Reference: WebLink] | Pseudodactylogyrus is a significant monogenean parasite of the gills of aquacultured European eels, and can cause severe gill pathology.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, effects of the crude extracts, fractions and compounds of exopleura of Ginkgo biloba against Pseudodactylogyrus were investigated under in vivo conditions by bio-assay guided isolation method. Four solvents (petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water) were applied for the extraction of exopleura of G. biloba. Among them, only the petroleum ether extract showed strong activity and therefore, subjected to further separation and purification using various chromatographic techniques. Two compounds showing potent activity were identified by comparing spectral data (IR, NMR, and EI-MS) with literature values to be ginkgolic acid C13:0 and Ginkgolic acid C15:1. They were found to be 100% effective at the concentration of 2.5mg l⁻1 and 6.0mg l⁻1, with ED₅₀ values of 0.72mg l⁻1 and 2.88mg l⁻1, respectively. In the 5-days safety test, ginkgolic acid C13:0 and Ginkgolic acid C15:1 were shown to be safe for healthy juvenile eels when the concentration were up to 10.0 and 18.0mg l⁻1, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS:
The two compounds exhibited potential results and can be explored as plant-derived antiparasitic for the control of Pseudodactylogyrus. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)