| In vitro: |
| Toxicol Ind Health. 2008 Apr;24(3):181-8. | | Metabolic activation of retronecine and retronecine N-oxide - formation of DHP-derived DNA adducts.[Pubmed: 18842697] |
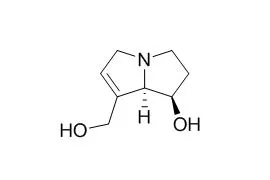
Retronecine is the necine base and the structurally smallest chemical of the Retronecine-type pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Although it has been reported that microsomal metabolism of Retronecine generated DHP as a metabolite, it was yet not known whether metabolism of Retronecine in vivo could generate DHP-derived DNA adducts and if formed, whether or not the levels of DNA adducts were comparable with those formed from the other tumorigenic Retronecine-type pyrrolizidine alkaloids, such as riddelliine, retrorsine, and monocrotaline.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this investigation, the in-vitro and in-vivo metabolic activation of Retronecine was studied. Rat liver microsomal metabolism of Retronecine in the presence of calf thymus DNA resulted in the formation of a set of DHP-DNA adducts. The metabolism of Retronecine N-oxide under similar conditions also formed the similar set of DHP-DNA adducts. The level of DNA adducts from Retronecine was enhanced when metabolism by liver microsomes from phenobarbital (PB)-induced rats were used. The DHP-DNA adducts were also found in the liver DNA of female F344 rats treated with Retronecine or Retronecine N-oxide. The highest level of the total DHP-DNA adducts was found in liver DNA from the rats treated with dehydroRetronecine (DHR). The order of the levels of DNA adducts in the liver DNA samples from rats treated with various pyrrolizidine alkaloids was: DHR > riddelliine > riddelliine N-oxide >> Retronecine > Retronecine N-oxide.
CONCLUSIONS:
The results indicate that 1) Retronecine can be metabolized to form DHP by rat liver microsomal enzymes and interacts with DNA to produce DHP-DNA adducts and 2) Retronecine N-oxide undergoes the biotransformation to the parent compound, Retronecine. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Nat Prod Commun. 2013 Nov;8(11):1545-6. | | Further evidence on the intramolecular lactonization in rat liver microsomal metabolism of 12-O-acetylated retronecine-type pyrrolizidine alkaloids.[Pubmed: 24427937] | We have previously found evidence of intramolecular lactonization in rat liver microsomal metabolism of isoline, a 12-O-acetylated pyrrolizidine alkaloid.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In this study, the metabolism of another 12-O-acetylated pyrrolizidine alkaloid, acetylduciformine, by the proposed transformation pathway was investigated under the same incubation conditions. Two deacetylated metabolites from acetylduciformine were isolated and purified by chromatographic methods, and further characterized based on their physical properties and spectral data. One metabolite (lankongensisine A) was the lactone of another one (duciformine).
CONCLUSIONS:
Both compounds were first obtained as hydrolyzed metabolites from acetylduciformine by rat liver microsomes. More importantly, the present study provided further evidence for the intramolecular lactonization in the microsomal metabolism of 12-O-acetylated Retronecine-type PAs. | | Toxicon. 1989;27(9):1059-64. | | A competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect retronecine and monocrotaline in vitro.[Pubmed: 2508272] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Antibodies to the nonesterified pyrrolizidine nucleus, Retronecine (155 mol.wt), were produced in rabbits and detected using an avidin-biotin antibody ELISA. A competitive ELISA for the detection of Retronecine and the cyclic diester monocrotaline was also developed using the antiserum produced against the hapten conjugate, Retronecine-bovine serum albumin. Retronecine was obtained by hydrolysis of monocrotaline, succinylated and directly coupled to bovine serum albumin or ovalbumin. Antibodies to the pyrrolizidine nucleus, Retronecine, can be detected within 5 min after the addition of substrate using the avidin-biotin ELISA.
CONCLUSIONS:
Competitive inhibition of antibodies to Retronecine is obtained by the addition of known amounts (0-11.42 micrograms/microliters) of either the homologous antigen, Retronecine, or the heterologous antigen, monocrotaline, however, Retronecine acts as the better competitor. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)