Licorice is the most used crude drug in Kampo medicines (traditional Chinese medicines modified in Japan). The extract of the medicinal plant is also used as the basis of anti-ulcer medicines for treatment of peptic ulcer.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
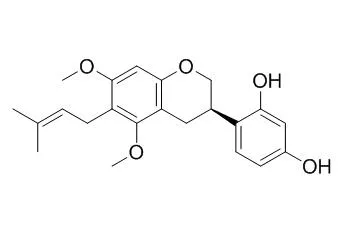
Among the chemical constituents of the plant, glabridin and glabrene (components of Glycyrrhiza glabra), licochalcone A (G. inflata), licoricidin and licoisoflavone B (G. uralensis) exhibited inhibitory activity against the growth of Helicobacter pylori in vitro. These flavonoids also showed anti-H. pylori activity against a clarithromycin (CLAR) and amoxicillin (AMOX)-resistant strain. We also investigated the methanol extract of G. uralensis. From the extract, three new isoflavonoids (3-arylcoumarin, pterocarpan, and isoflavan) with a pyran ring, gancaonols A[bond]C, were isolated together with 15 known flavonoids. Among these compounds, vestitol, licoricone, 1-methoxyphaseollidin and gancaonol C exhibited anti-H. pylori activity against the CLAR and AMOX-resistant strain as well as four CLAR (AMOX)-sensitive strains. Glycyrin, formononetin, isolicoflavonol, Glyasperin D, 6,8-diprenylorobol, gancaonin I, dihydrolicoisoflavone A, and gancaonol B possessed weaker anti-H. pylori activity.
CONCLUSIONS:
These compounds may be useful chemopreventive agents for peptic ulcer or gastric cancer in H. pylori-infected individuals. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)