| Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 12;108(28):11596-601. |
| Dehydro-alpha-lapachone, a plant product with antivascular activity.[Pubmed: 21709229] |
Antivascular agents have become a standard of treatment for many malignancies. However, most of them target the VEGF pathway and lead to refractoriness.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
To improve the diversity of options for antivascular therapy, we applied a high-throughput screen for small molecules targeting cell adhesion. We then assayed the resulting antiadhesion hits in a transgenic zebrafish line with endothelial expression of EGFP (Tg(fli1:EGFP)(y1)) to identify nontoxic molecules with antivascular activity selective to neovasculature. This screen identified Dehydro-alpha-lapachone (DAL), a natural plant product. We found that Dehydro-alpha-lapachone inhibits vessel regeneration, interferes with vessel anastomosis, and limits plexus formation in zebrafish. Furthermore, Dehydro-alpha-lapachone induces vascular pruning and growth delay in orthotopic mammary tumors in mice.
CONCLUSIONS:
We show that Dehydro-alpha-lapachone targets cell adhesion by promoting ubiquitination of the Rho-GTPase Rac1, which is frequently up-regulated in many different cancers. |
| Pest Manag Sci. 2006 May;62(5):414-8. |
| Dehydro-alpha-lapachone isolated from Catalpa ovata stems: activity against plant pathogenic fungi.[Pubmed: 16550502] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
The methanol extract of stems of Catalpa ovata G Don exhibits potent in vivo antifungal activity against Magnaporthe grisea (Hebert) Barr (rice blast) on rice plants, Botrytis cinerea Pers ex Fr (tomato grey mould) and Phytophthora infestans (Mont) de Bary (tomato late blight) on tomato plants, Puccinia recondita Rob ex Desm (wheat leaf rust) on wheat plants and Blumeria graminis (DC) Speer f. sp. hordei Marchal (barley powdery mildew) on barley plants.
CONCLUSIONS:
An antifungal substance was isolated and identified as Dehydro-alpha-lapachone from mass and nuclear magnetic resonance spectral data. It completely inhibited the mycelial growth of B. cinerea, Colletotrichum acutatum Simmonds, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides Simmonds, M. grisea and Pythium ultimum Trow over a range of 0.4-33.3 mg litre(-1). It also controlled the development of rice blast, tomato late blight, wheat leaf rust, barley powdery mildew and red pepper anthracnose (Colletotrichum coccodes (Wallr) S Hughes).
The chemical was particularly effective in suppressing red pepper anthracnose by 95% at a concentration of 125 mg litre(-1). |
| Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):311-3. |
| Microbial transformations of natural antitumor agents: conversion of lapachol to dehydro-alpha-lapachone by Curvularia lunata.[Pubmed: 574750] |
METHODS AND RESULTS:
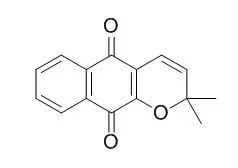
Microbial transformation of lapachol, a naturally occurring naphthoquinone, was carried out by Curvularia lunata (NRRL 2178). The fungus brings about oxidative cyclization of the substrate to Dehydro-alpha-lapachone, which was isolated and characterized by nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectral analyses; its structure was verified by chemical synthesis.
CONCLUSIONS:
The metabolite is a naturally occurring chromene possessing antibacterial and antitumor activities. |





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)