| Description: |
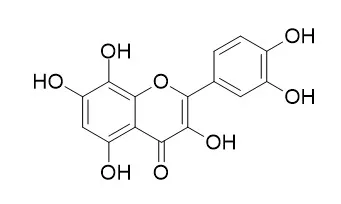
Gossypetin has anti-mutagenic, anti-atherosclerotic, antioxidant, as well as cytoprotective and antimicrobial effects, it inhibits bone resorption through down-regulating lysosomal cathepsin K activity and autophagy-related protein induction in actin ring-bearing osteoclasts. Gossypetin ameliorates ionizing radiation-induced oxidative stress in mice liver, it shows radioprotective action against gamma (γ)-radiation-induced oxidative stress. Gossypetin is an inducer of apoptotic and autophagic cell death in LNCaP cells, and provide a new mechanism for its anticancer activity.
|
| In vitro: |
| Journal of Functional Foods, 2016, 24:390-402. | | Dietary compound gossypetin inhibits bone resorption through down-regulating lysosomal cathepsin K activity and autophagy-related protein induction in actin ring-bearing osteoclasts[Reference: WebLink] | Gossypetin, usually isolated from the flowers and the calyx of Hibiscus sabdariffa, possesses anti-microbial and anti-atherosclerotic effects. However, anti-osteoporotic effects of Gossypetin have not been elucidated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Gossypetin attenuated RANKL-induced multinucleated osteoclast formation with enhanced TRAP activity and blunted bone resorption active in osteoclasts. Gossypetin inhibited the actin ring formation and αvβ3 integrin induction for sealing zones. This compound suppressed the induction of CAII, V-ATPase, ClC-7 and Ae2, all required for secretion of proton and chloride ions into resorption lacunae. Furthermore, Gossypetin reduced lysosomal cathepsin K transcription and MMP-9 activity, blunting accumulation of lysosomes in osteoclasts displaying an actin ring. The presence of Gossypetin deterred the induction of Rab7, and Atg12–Atg5 conjugate and Atg7 involved in LC3 lipidation, all prerequisites to osteoclast ruffled border formation.
CONCLUSIONS:
These observations demonstrate for the first time that Gossypetin was effective in retarding ruffled border formation and acidification in a sealed microenvironment of osteoclast resorption lacunae. | | Medicinal Chemistry,2016, 6(2). | | Protective Role of Gossypetin against Cyclophosphamide Toxicity in Human Lymphocyte Culture In vitro[Reference: WebLink] | Gossypetin is a flavonoid which has anti-mutagenic, anti-atherosclerotic, antioxidant, as well as cytoprotective and antimicrobial effects. The objective of this study was to investigate the cytoprotective role of Gossypetin (GP) against cyclophosphamide (CP) toxicity in the human lymphocyte culture.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Cytotoxic, necrotic and apoptotic effects of CP (1mM), GP (25, 50 and 100 μM) and combination of them (CP+GP) were studied by using MTT assay and Flow cytometry analysis. It was detected that CP significantly decreased cell viability rate via arresting cell cycle and increasing apoptosis/necroptosis. However, GP treatment reduced negative effects of CP at different concentrations. The most effective concentration of GP against CP toxicity was 25 μM. This concentration GP increased live cell number and cell viability, in addition decreased necrotic and late apoptotic cell quantity which were treated with CP.
CONCLUSIONS:
These results suggest that GP could attenuate the cytotoxic effects of CP and protect the healthy cells when it is used during chemotherapy. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)