| Description: |
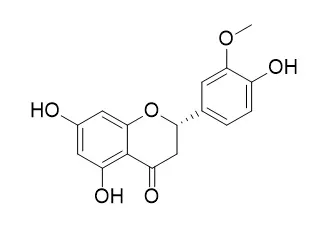
Homoeriodictyol, a naturally occurring, bitter-masking flavanone, as a promising agent to increase appetite and food intake. The flavanone homoeriodictyol can increase SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decrease serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.
|
| Targets: |
GLUT | 5-HT Receptor | Sodium Channel |
| In vitro: |
| PLoS One. 2017 Feb 13;12(2):e0171580. | | The flavanone homoeriodictyol increases SGLT-1-mediated glucose uptake but decreases serotonin release in differentiated Caco-2 cells.[Pubmed: 28192456 ] | Flavanoids and related polyphenols, among them hesperitin, have been shown to modulate cellular glucose transport by targeting SGLT-1 and GLUT-2 transport proteins.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
We aimed to investigate whether Homoeriodictyol, which is structurally related to hesperitin, affects glucose uptake in differentiated Caco-2 cells as a model for the intestinal barrier. The results revealed that, in contrast to other polyphenols, the flavanon Homoeriodictyol promotes glucose uptake by 29.0 ± 3.83% at a concentration of 100 μM. The glucose uptake stimulating effect was sensitive to phloridzin, but not to phloretin, indicating an involvement of the sodium-coupled glucose transporter SGLT-1, but not of sodium-independent glucose transporters (GLUT). In addition, in contrast to the increased extracellular serotonin levels by stimulation with 500 mM D-(+)-glucose, treatment with 100 μM Homoeriodictyol decreased serotonin release by -48.8 ± 7.57% in Caco-2 cells via a phloridzin-sensitive signaling pathway. Extracellular serotonin levels were also reduced by -57.1 ± 5.43% after application of 0.01 μM Homoeriodictyol to human neural SH-SY5Y cells.
CONCLUSIONS:
In conclusion, we demonstrate that Homoeriodictyol affects both the glucose metabolism and the serotonin system in Caco-2 cells via a SGLT-1-meditated pathway. Furthermore, the results presented here support the usage of Caco-2 cells as a model for peripheral serotonin release. Further investigations may address the value of Homoeriodictyol in the treatment of anorexia and malnutrition through the targeting of SGLT-1. |
|
| In vivo: |
| Mol Nutr Food Res. 2017 Aug 21. | | Appetite-Inducing Effects of Homoeriodictyol: Two Randomized, Cross-Over Interventions.[Pubmed: 28834253 ] | Anorexia of aging, characterized by a decrease in appetite and/or food intake, is a major risk factor of under-nutrition and adverse health outcomes in elderly people. Recent in vitro evidence suggests Homoeriodictyol (HED), a naturally occurring, bitter-masking flavanone, as a promising agent to increase appetite and food intake.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
In two cross-over intervention trials, 30 mg NaHED, either solely (n = 10, Study I) or in combination with a 75 g glucose load (n = 17, study II) were administered to healthy adult subjects. Ratings of hunger were assessed at fasting and either 30 min (Study I) or 120 min (Study II) post intervention. Ad libitum energy intake from a standardized breakfast and plasma changes in hunger-/satiety-associated hormones PYY, GLP-1, ghrelin and serotonin were determined after blood drawings. Effects were more pronounced when NaHED was administered in combination with 75 g glucose since ad libitum energy (+ 9.52 ± 4.60%) and protein (+ 7.08 ± 7.97%) intake as well as plasma ΔAUC ghrelin values increased in study II solely, whereas plasma serotonin concentrations decreased after both interventions.
CONCLUSIONS:
NaHED demonstrated appetizing effects in healthy adults when administered with a glucose load. Long-term intervention studies are warranted to verify these effects in compromised subjects. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)