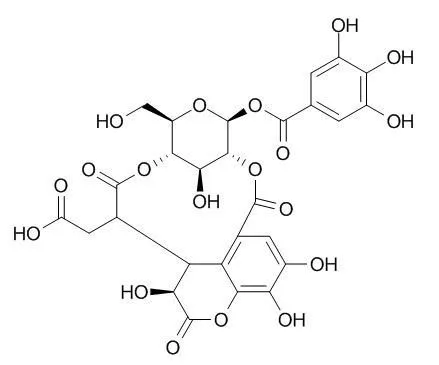
| Description: |
Chebulanin is a topoisomerase I inhibitor, it inhibits the calcineurin pathway in C. neoformans. Chebulanin exhibits potent antifungal activity against various human pathogenic fungi with minimum inhibitory concentrations ranging from 0.25 to over 64 μg/ml. Chebulanin shows strong radical scavenging activity, good potency to chelate Fe2⁺ and good inhibition ability of lipid peroxidation. Chebulanin is a strong therapeutic alternative for the treatment of rheumatism arthritis, it suppresses the expression of inflammatory mediators and prevents cartilage destruction and bone erosion in mice.Chebulanin has anti-cancer acrtivity, it has apparent capacities of inhibiting the survival of MCF-7 human cancer cell line. |
| Targets: |
TNF-α | IL Receptor | MMP(e.g.TIMP) | COX | Antifection |
| In vitro: |
| Food Chemistry, 2011 , 126 (1) :277-282. | | Antioxidant and antiproliferative capacities of phenolics purified from Phyllanthus emblica L. fruit[Reference: WebLink] |
Phyllanthus emblica is a widely distributed tropical medicinal plant with good therapeutic properties.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Gallic acid, ellagic acid, mucic acid 1,4-lactone 3-O-gallate, isocorilagin, Chebulanin, chebulagic acid and mallotusinin were isolated and purified from this plant. The antioxidant activities of these compounds were evaluated by in vitro models of scavenging superoxide anion radicals, DPPH radicals and ABTS radicals, chelating ability of ferrous ion and inhibition capability of Fe (II)-induced lipid peroxidation, respectively. The results revealed that all the tested phenolics showed strong radical scavenging activity, good potency to chelate Fe2+ and good inhibition ability of lipid peroxidation. Amongst mallotusinin and mucic acid 1,4-lactone 3-O-gallate were reported for the first time to have antioxidant activity. In addition, the in vitro antiproliferative activities of those phenolics against MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines were assessed.
CONCLUSIONS:
Although the growth inhibition values induced by different phenolics on MCF-7 cell line yielded different effects, all the tested phenolics had apparent capacities of inhibiting the survival of MCF-7 human cancer cell line. |
|
| In vivo: |
| PLoS One. 2015 Sep 24;10(9):e0139052. | | Anti-Arthritic Effect of Chebulanin on Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Mice.[Pubmed: 26402786 ] | Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic degenerative autoimmune disease characterized by persistent inflammation of synovial membranes, which leads to cartilage destruction and bone erosion. To date, there are no effective therapies to slow the progress of this degenerative condition.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
Here, we evaluate the anti-arthritic effect of Chebulanin, an abundant anti-inflammatory agent isolated from Terminalia chebula, in collagen induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice by intragastric administration. Arthritic severity was scored by performing histopathological evaluation of the joints and measuring the expression of inflammatory cytokines and relative enzymes by immunohistochemical staining. In parallel, bone destruction and erosion were confirmed by micro-CT. Our data revealed that Chebulanin significantly improved the severity of arthritis. Specifically, the histopathological characteristics of the tissues were improved and expression of TNF-α, IL-6, MMP-3 and COX-2 in the paws and joints of the treated mice decreased in a dose-dependent manner compared with control mice. Furthermore, micro-CT analysis revealed that Chebulanin induced a dose-dependent reduction in cartilage destruction and bone erosion.
CONCLUSIONS:
Taken together, our findings suggest that Chebulanin suppresses the expression of inflammatory mediators and prevents cartilage destruction and bone erosion in mice. Therefore, Chebulanin is a strong therapeutic alternative for the treatment of RA. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)