| In vitro: |
| Molecules, 2018, 23(11). | | Inhibition of Osteoarthritis-Related Molecules by Isomucronulatol 7-O-β-d-glucoside and Ecliptasaponin A in IL-1β-Stimulated Chondrosarcoma Cell Model.[Reference: WebLink] | Osteoarthritis (OA) is the common form of arthritis and is characterized by
disability and cartilage degradation. Although natural product extracts have been reported to
have anti-osteoarthritic effects, the potential bioactivity of Ryupunghwan (RPH), a traditional
Korean medicinal botanical formula that contains Astragalus membranaceus, Turnera diffusa,
Achyranthes bidentata, Angelica gigas, Eclipta prostrata, Eucommia ulmoides, and Ilex paraguariensis,
is not known well.
Therefore, the inhibitory effects of single compounds isolated from RPH on the
OA-related molecules were investigated using IL-1β-stimulated chondrosarcoma SW1353 (SW1353)
cell model.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
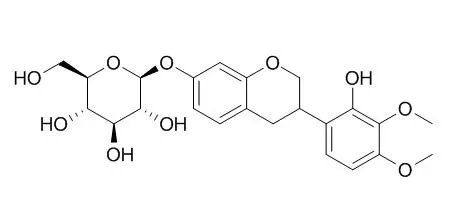
Two bioactive compounds, isomucronulatol 7-O-β-D-glucoside (Isomucronulatol 7-O-glucoside, IMG) and ecliptasaponin
A (ES) were isolated and purified from RPH using column chromatography, and then the structures
were analyzed using ESI-MS, 1H-NMR, and 13C-NMR spectrum. The expression or amount of
matrix metalloproteinase 13 (MMP13), COX1/2, TNF-α, IL-1β or p65 was determined by RT-PCR,
Western blot, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). RPH pretreatment reduced the
expression and amounts of MMP13, and the expression of collagen II, COX1/2, TNF-α, IL-1β or
p65, which were increased in IL-1β-stimulated SW1353 cells. IMG reduced the expression of all
OA-related molecules, but the observed inhibitory effect was less than that of RPH extract. The other
single compound ES showed the reduced expression of all OA-related molecules, and the effect
was stronger than that in IMG (approximately 100 fold). Combination pretreatment of both single
components remarkably reduced the expression of MMP13, compared to each single component.
CONCLUSIONS:
These synergic effects may provide potential molecular modes of action for the anti-osteoarthritic
effects of RPH observed in clinical and animal studies. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)