| In vitro: |
| J Agric Food Chem. 2013 Nov 6;61(44):10507-15. | | Qualitative and quantitative analysis of phenolics in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities.[Pubmed: 24151872] | The phenolic profiles of Tetrastigma hemsleyanum leaf extracts by different solvents (80% methanol, ethyl acetate and hexane) and their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities were investigated.
METHODS AND RESULTS:
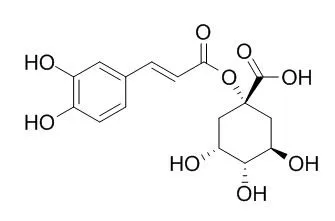
Thirteen phenolic compounds (3-caffeoylquinic acid, 5-caffeoylquinic acid, 1-Caffeoylquinic acid, 5-p-coumaroylquinic acid, isoorientin-2″-O-rhamnoside, isoorientin, orientin-2″-O-rhamnoside, orientin, 1-p-coumaroylquinic acid, vitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, isovitexin-2″-O-rhamnoside, vitexin and isovitexin) were identified in T. hemsleyanum leaves for the first time, and six of them were quantified using a combination of LC-QTOF-MS and LC-QqQ-MS techniques. It was found that 80% methanol extract exhibited the highest antioxidant activities.
CONCLUSIONS:
This paper provides a complete picture of phenolics in T. hemsleyanum leaves and relates them to their antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. | | Anal Biochem . 2018 Apr 15;547:52-56. | | PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor screening of caffeoylquinic acid compounds using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy[Pubmed: 29428377] | | Abstract
Following the FDA approval of three monoclonal antibodies of PD-1/PD-L1, this pathway has become a promising target for cancer treatment. Currently small-molecule inhibitors have not been extensively investigated, and appropriate screening methods for such inhibitors are urgently required. In this study, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology was used to evaluate the affinity and competitive inhibition of nine caffeoylquinic acid compounds (CQAs) against PD-1/PD-L1. As a result, four small molecules including 1-CQA, 3-CQA, 4-CQA and 5-CQA were determined as PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. This study provided an efficient method for screening small-molecule inhibitors targeting PD-1/PD-L1 pathway.
Keywords: Caffeoylquinic acid compounds; PD-1; PD-L1; Small-molecule inhibitors; Surface plasmon resonance. |
|





 Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019)
Cell. 2018 Jan 11;172(1-2):249-261.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.019.IF=36.216(2019) Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019)
Cell Metab. 2020 Mar 3;31(3):534-548.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.01.002.IF=22.415(2019) Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)
Mol Cell. 2017 Nov 16;68(4):673-685.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.022.IF=14.548(2019)